In today’s ever-changing business landscape, organizations are continuously confronted with challenges like supply chain disruptions, regulatory pressures, geopolitical tensions, and more. In such situations, the absence of a capacity requirement planning framework can result in:
- Shortage of skilled personnel
- Last-minute firefighting for the right resources
- Inflated costs due to urgent hiring
This can result in subpar project outcomes, unhappy clients, missed business opportunities, and increased financial pressure. An efficient capacity requirement planning process allows firms to predict and resolve resource bottlenecks, helping to build a robust talent pool.
Read this blog to learn how capacity requirement planning can help secure the necessary resources ahead of the curve and drive sustainable growth.
Let us begin with the capacity requirement planning definition!
What is Capacity Requirement Planning?
Capacity requirement planning is a process of assessing an organization’s capacity or ability to meet pipeline project demands. In simple terms, it involves assessing whether the firm’s existing resource pool is sufficient to meet upcoming project requirements.
The process involves forecasting demand by considering factors like scope, budget, skill sets, equipment, timeframe, etc. It also involves critically assessing the internal talent pool and comparing existing resources with anticipated requirements.
If capacity is insufficient, resource managers can take appropriate actions to close the demand gaps. Thus, capacity requirement planning helps ensure the timely availability of competent resources, avoids under-allocation or over-utilization of the workforce, and improves project outcomes.
Now that you know what capacity requirement means, let us explore its various types.
Types of Capacity Requirement Planning
Below are the three main types of capacity requirement planning every organization should rely on.
Workforce Capacity Planning
Workforce capacity planning involves determining if the organization’s existing staff can accomplish the short and long-term objectives of the business. This involves evaluating organizational capacity based on resource skills, competencies, experience, location, and availability, then aligning these with upcoming demands to ensure efficient, timely, and budget-compliant delivery.
Product Capacity Planning
Product capacity planning is the process of assessing the production capacity needed by a business to meet changing demands for its products. It involves forecasting the production volume and balancing the available resources (like labor, machinery, and raw materials) with customer demand. This ensures that products are manufactured efficiently without over or under-production.
Tool Capacity Planning
Tool capacity planning is a process that ensures the organization has sufficient tools, equipment, or machinery needed to meet project demands efficiently. This analysis helps businesses to secure the necessary resources at the right time and cost, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted workflows. This type of planning is particularly crucial in industries like manufacturing, construction, and automotive, where specialized tools are essential for efficient operations.
Let’s explore why capacity requirement planning is crucial across various industries.
Read More: What is Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Business Efficiency
Why is Capacity Requirement Planning Critical for Different Industries?
Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) is crucial for businesses to optimize resource allocation, reduce downtime, and avoid shortages or excess capacity. Given below are how CRP helps in some of the major industries.
Audit & Accounting/ Legal Firms
Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) is essential for audit, accounting, and legal firms to ensure the right number of skilled professionals are available to meet client deadlines. It also helps manage seasonal workload fluctuations, such as during tax season or year-end audits, without compromising quality or compliance. By optimizing staff allocation, CRP helps maximize billable hours and maintain a balanced workload, improving employee satisfaction and retention.
AEC Industry
Like any other industry, resources are the focal point of AEC projects. As a result, CRP ensures that skilled labor, equipment, and materials are available to meet project demands. It also helps in effectively managing the ramp-up and ramp-down of resources throughout various project phases. By accurately forecasting resource requirements, CRP helps AEC firms control costs, streamline workflows, and maintain project schedules.
Read More: How to Implement Effective Resource Capacity Planning in AEC Industry?
Professional Service Industry
For professional services firms, including consulting, marketing, and design agencies, CRP is vital for optimizing the utilization of specialized talent. It helps align staff availability with project timelines to maximize billable hours and profitability. CRP also enables these firms to scale resources up or down based on client demands. This leads to timely project delivery, higher client satisfaction, and better talent retention.
IT Industry
In the IT industry, CRP ensures that technical resources such as developers, testers, and infrastructure are optimally allocated to support agile development cycles and digital transformation initiatives. By forecasting resource requirements, CRP helps IT teams manage workloads across multiple projects, reduce bottlenecks, and minimize the risk of missed deadlines. Additionally, it optimizes infrastructure utilization, ensuring cost-effective management of hardware, cloud resources, and networks, thereby enhancing overall project efficiency.
Read More: How Does the IT Industry Benefit from Efficient Workforce Planning?
Now, let’s examine an example of capacity requirement planning.
Capacity Requirement Planning: A Practical Example
Let’s consider a construction firm preparing to kick off three major infrastructure projects next quarter. Based on the scope of work for each project, the estimated requirements for equipment and skilled labor are as follows:
- Project A – 1,500 hours of crane usage and 2,000 hours of skilled labor.
- Project B – 1,200 excavator time and 1,800 hours of general labor.
- Project C – 1,800 hours of bulldozer operation and 2,200 hours of specialized construction labor.
This results in a total demand of 4,500 equipment hours (1,500 + 1,200 + 1,800) and 6,000 labor hours (2,000 + 1,800 + 2,200) for the upcoming quarter.
Upon reviewing the current capacity, the firm finds they have 3,800 equipment hours and 5,400 labor hours available.
The capacity shortfall is calculated as follows: Expected Demand – Available Capacity
- Equipment shortage: 4,500 (demand) – 3,800 (available) = 700 equipment hours
- Labor shortage: 6,000 (demand) – 5,400 (available) = 600 labor hours
To bridge this gap, the firm considers renting additional equipment, hiring temporary labor, or redistributing resources from other projects. This targeted capacity requirement planning enables the construction firm to stay prepared and minimize delays, ensuring seamless project delivery.
The next section outlines the steps involved in the capacity requirement planning process.
Read More: What is Resource Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Every Project Manager
Steps to Follow During Capacity Requirements Planning
Having a solid capacity requirement plan is crucial to ensure your organization is well-prepared to meet demand. Here’s a step-by-step guide that will help you effectively align your resources with business needs:
Step 1: Foresee Upcoming Demand Based on Resource Types
The first step in capacity requirements planning is accurately forecasting future demand for different types of resources, whether it’s personnel, equipment, or technology. By understanding the specific skills, tools, or materials required, organizations can prepare for peak periods, prevent shortages, and align resources with project timelines. An effective demand forecast allows businesses to proactively plan for resource allocation, minimizing the risk of disruptions.
Step 2: Evaluate Existing Capacity
Once future demand is forecasted, it’s crucial to assess the current capacity available within the organization. This includes evaluating the existing workforce’s skill levels, equipment availability, and overall resource utilization rates. Managers should also consider scheduled leaves, contract expirations, and ongoing hiring processes to ensure a precise evaluation. By assessing current capacity, firms can decide whether their existing resources are sufficient to meet future demands or if additional resources are required.
Read More: How to Measure Resource Capacity and Demand?
Step 3: Identify & Bridge the Demand Gaps
After comparing forecasted demand with existing capacity, organizations may identify gaps such as shortages or excess of resources. In case of resource shortage, managers can upskill current employees, implement out-rotation and backfill strategies, or recruit a permanent or contingent workforce. Alternatively, if there is a resource surplus, they can expedite project timelines or sell extra capacity at a discounted rate. Therefore, effectively bridging these gaps is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage and meeting client expectations.
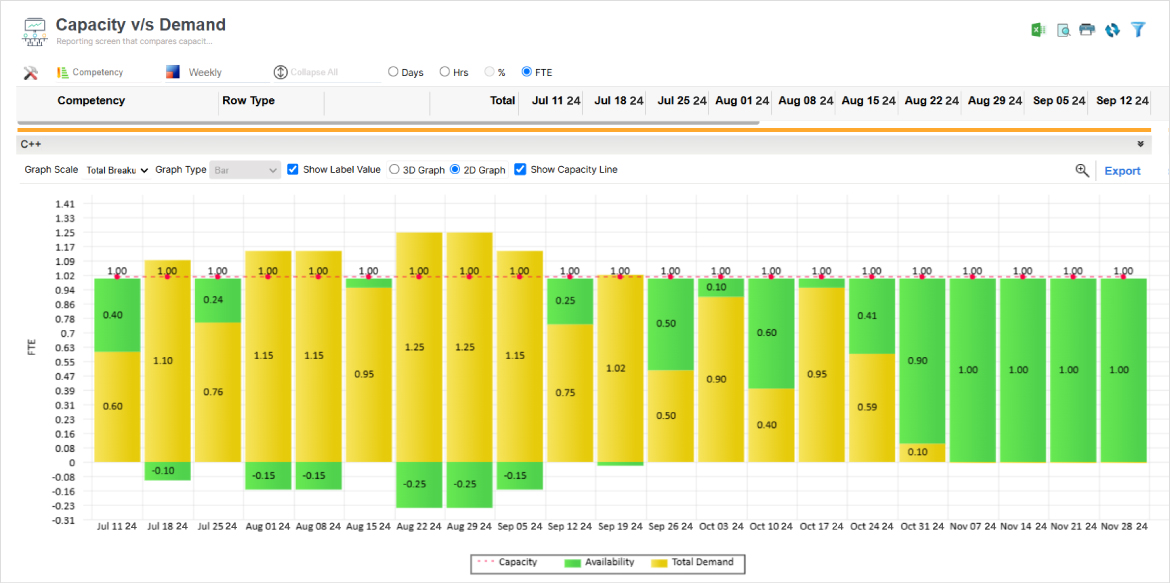
SAVIOM’s advanced Capacity vs. Demand graph enables managers to predict and bridge demand gaps, ensuring smooth resource allocation and avoiding last-minute disruptions.
Step 4: Account for Constraints & Create Contingency Plans
Capacity planning isn’t just about meeting demand; it also helps plan for potential constraints, such as unexpected project scope changes, employee absences, budget limits, supply chain issues, or regulatory compliance. Developing contingency plans enables firms to adapt quickly if things don’t go as planned. This could involve strategies such as cross-training employees, keeping a reserve of essential supplies, or having backup vendors ready.
Step 5: Review and Adjust Plans Regularly
Capacity planning is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing and adjusting capacity plans based on real-time data, project changes, or shifts in market conditions ensures that organizations remain agile and prepared for evolving demands. By keeping the plan dynamic and responsive, businesses can optimize resource utilization, improve profitability, and drive long-term growth.
Bottom Line
Capacity Requirement Planning (CRP) is more than a process—it’s a strategic driver for projects to align resources with demand. Whether allocating resources for short-term projects or planning for long-term goals, CRP is crucial for any business seeking to maintain consistency, minimize overheads, and optimize performance in today’s competitive environment.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management











