“Agile teams produce a continuous stream of value, at a sustainable pace, while adapting to the changing needs of the business.” – Elisabeth Hendrickson.
Rightly said! This quote encapsulates the core of agile methodology: consistently delivering value while staying adaptable to changing demands. Central to this flexibility is agile capacity planning, a vital practice that helps businesses align resources with product backlogs and achieve successful project outcomes.
Effective agile capacity planning gives managers clear insights into available resources, enabling them to address demand fluctuations with each sprint. It ensures the timely allocation of skilled resources, promotes balanced workloads, and enhances overall team productivity. This approach ultimately delivers high-quality sprint outcomes, surpassing client expectations and sustaining a competitive market edge.
This blog delves into the details of agile capacity planning, covering its benefits, challenges, and practical tips for effective implementation.
But first, let’s begin with the basics!
What is Agile Capacity Planning?
Agile capacity planning entails evaluating and aligning a scrum team’s available capacity with the product backlog for a particular sprint or iteration. This process involves thoroughly evaluating your team’s skills, competencies, availability, and other factors in relation to the sprint’s duration and planned activities.
If any resource imbalances, i.e., excesses or shortages, are identified, managers can apply corrective measures to create an optimal team before the sprint begins. Consequently, this ensures enhanced team productivity, smooth sprint transitions, and on-time project delivery.
Let’s explore this further with an example-
Agile Software Development: A Capacity Planning Example
An e-commerce startup plans to build a mobile app to streamline browsing, purchasing, and order tracking. The project is divided into five sprints, each lasting three weeks, to deliver a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in four months.
To ensure the team can meet sprint objectives, it’s essential to assess the capacity needed for each sprint. Let’s start by evaluating the workload for sprint 1.
For Sprint 1, the backlog activities include setting up the development environment, creating user personas, building app architecture, and designing wireframes.
With the sprint lasting three weeks, the estimated effort totals 120 hours, broken down as follows:
- 80 hours for development (10 days × 8 hours/day)
- 24 hours for design (3 days × 8 hours/day)
- 16 hours for QA (2 days × 8 hours/day)
The resource requirements for this sprint include three developers, two designers, and one QA.
Upon evaluating the internal capacity, it was determined that there is a shortage of developers, particularly in backend integration and app architecture design. To address this gap, the manager must take necessary resourcing measures, such as hiring additional resources, training or retraining existing staff, etc., to ensure the sprint progresses on schedule.
Agile capacity planning is an ongoing process, not a one-off activity. Just as we performed the demand gap analysis for sprint 1, it must be carried out for subsequent sprints (2, 3, 4, 5). This will help managers to make necessary capacity adjustments and ensure timely project completion.
Now that you know the definition, let’s learn about the various benefits of agile capacity planning.
Read more: What is Agile Project Management & How to Effectively Manage Resources?
7 Key Benefits of Agile Capacity Planning
Some key benefits are given below. Read on:
Helps in Better Sprint Planning & Delivery
Agile capacity planning enables accurate forecasting of pipeline opportunities and sprint-specific demands. Accordingly, managers can conduct a capacity vs. demand analysis across various attributes like role, competencies, location, etc., and secure suitable resources. This helps avoid frequent hiring/firing cycles, align the team with sprint goals, and ensure seamless delivery.
Improves Resource Allocation at Sprint Level
Efficient agile capacity planning helps managers to forward plan and create a competent resource pool for each sprint. This enables managers to assign the best- visible-best-fit resource rather than first-available-first-fit, preventing talent mismatches, decreased productivity, etc. Additionally, resources can be proactively reallocated as project requirements evolve, ensuring seamless execution.
Read more: What is Resource Allocation? A Comprehensive Guide for Project Success
Reduces Risk of Over-Utilization and Burnout
A robust agile capacity planning process enables managers to align workforce availability with sprint demands, preventing under/overallocation of resources. It ensures balanced workload distribution, keeping scrum teams productive without overburdening them. This approach reduces stress, boosts morale, supports consistent performance, and improves overall billability.
Increases Flexibility to Adapt to Change
Agile capacity planning embeds flexibility into sprint schedules, enabling teams to respond swiftly to shifting priorities in real-time. When new requirements arise, managers may once again reassess their capacity against the sprint backlog and acquire resources as needed. This ensures scrum teams remain efficient and well-prepared to deliver value as project needs evolve.
Enhances Decision-Making in Real-Time
Effective agile capacity planning improves sprint predictability by aligning tasks with the scrum team’s available capacity, ensuring work stays on track and within budget. Further, with each iteration, the scrum master gains better insights into team performance, allowing for more accurate capacity forecasts. This enables data-driven decision-making and adjustments, resulting in more successful sprint outcomes.
Facilitates Better Resource Risk Management
Agile capacity planning enables managers to assess sprint capacity and backlog in advance. This helps in the early identification of resource risks, such as employee shortages, skill gaps, sub-optimal utilization, etc., that could disrupt sprint timelines and deliverables. With this foresight, managers can implement contingency measures like training, maintaining resource buffers, etc., to ensure sprint progress.
Read more: How to Mitigate Resource Risk in Project Management?
Having understood the benefits, let’s explore the difference between team capacity and team velocity.
Team Capacity vs. Team Velocity: The Difference
Understanding the difference between team capacity and team velocity is crucial for effective capacity planning in agile. Here’s a breakdown of how these two concepts differ and how they impact sprint planning and execution.
Below mentioned are the significant differences –
| Aspect | Team Velocity | Team Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the actual work completed in a sprint | Measures the potential work hours available in a sprint |
| Metric Type | Historical (based on past performance) | Forward-looking (based on availability) |
| Purpose | Helps in estimating future work based on past trends | Helps in planning workload based on team availability |
| Units of Measurement | Story points, user stories, or other work units | Hours or days of effort |
| Focus | Reflects team productivity | Reflects team availability |
| Used For | Sprint planning, forecasting project timelines | Capacity planning, workload balancing |
| Flexibility | May fluctuate due to factors like task complexity | Varies based on team size, availability, and commitments |
| Impact of Changes | Affected by changes in team performance or task types | Affected by team size, leave, and resource availability |
Read more: How to Measure Resource Capacity and Demand?
Now that we have understood the difference, let’s learn how to plan capacity in agile.
How to Calculate Team Capacity for Each Sprint?
To calculate team capacity for each sprint, let’s walk through the steps using an IT development team as an example. Here’s how you can apply the process practically:
Estimate the Sprint Duration
Firstly, determine the total number of working days within the sprint. Consider the scope of sprint activities, their dependencies, and the team’s overall workload to ensure the sprint timeline is realistic and achievable.
Sprint durations are typically 1-4 weeks, depending on the project’s complexity and team preferences. Let’s assume the IT development team operates on a 2-week sprint cycle, excluding weekends. This gives a total of 10 working days.
Consider the Standard Hours Per Day
Next, calculate the available hours for each team member based on their work schedules (full-time or part-time). For a team of 5 developers working 8 hours per day:
Individual capacity for one sprint: 8 hours/day × 10 days = 80 hours.
Total capacity for the team: 80 hours × 5 members = 400 hours.
For consistency, you can even convert these hours into Full-Time Equivalents (FTEs). Here’s how to calculate FTE for the 400 total hours for a team of developers:
FTE = Total Team Hours / Standard Capacity of One Full-Time Employee= 400 Hours / 80 Hours = 5.0 FTE
Evaluate Team’s Utilization Rate
In the third step, track how effectively each member’s time will be spent on sprint tasks compared to their total capacity. As we know, not all working hours are spent on development or core project tasks. Time may be spent in:
- Team meetings (daily stand-ups, sprint planning, retrospectives).
- Administrative tasks (email communication, documentation).
- Cross-functional activities (knowledge sharing, mentoring).
In this case, let’s assume the development team operates at a 75% utilization rate.
Then, Formula for Utilization Rate = (Productive Hours / Total Team Hours) × 100
Productive Hours = Total Team Hours × Utilization Rate
= 400 hours x 75% = 300 hours
This means that of the 400 available hours, only 300 hours can be allocated for sprint tasks.
Read more: How to Track Resource Utilization?
Determine the Team’s Time-Off, Holidays, etc.
In every sprint, team availability may fluctuate due to absences, such as vacations, unplanned leaves, or public holidays. It’s essential to account for these variables when calculating sprint capacity. Overlooking these factors can lead to unrealistic sprint commitments, task delays, and overburdening of available team members.
This also allows the manager to adjust workloads for the team or bring in backup resources if necessary. Proactively planning for such absences helps mitigate risks and maintain a steady workflow during the sprint.
Sum the Capacity for All Team Members
Once you’ve considered individual work schedules, utilization rates, and absences, sum up the available capacities of all team members. This provides a realistic view of the total hours the team can commit to during the sprint.
For a development team, this aggregated capacity forms the foundation of task allocation. It ensures that sprint goals are set within achievable limits, fostering a smoother workflow and higher team efficiency.
Read more: What is Capacity Management & How to do it Effectively?
Now, let’s look at the various challenges of agile team capacity planning.
Challenges of Capacity Planning for Agile Teams
Capacity planning challenges, if not addressed proactively, can lead to inefficiencies, uneven workloads, and unmet goals. Let’s examine them –
Inability to Foresee Fluctuating Resource Demands
Agile teams operate in dynamic environments where unforeseen client requests, regulatory changes, or shifting priorities can arise mid-sprint. These changes often expand the project scope. As a result, the initial capacity plan for the sprint may no longer align with the new needs. The inability to adapt quickly can result in either resource shortages or overburdened team members, ultimately compromising the sprint’s success.
Read more: What is Capacity Requirement Planning, and Why is it Important?
Poorly Defined Tasks in Sprint Backlog
When tasks in the sprint backlog lack clarity, estimating the time and effort required becomes challenging. This ambiguity disrupts capacity planning, as managers cannot accurately determine how much work can be accomplished within the sprint. As a result, the manager either overestimates or underestimates the workload, leading to misallocation and compromising the ability to meet sprint goals.
Inability to Manage Team Dependencies
Agile projects depend on collaboration among cross-functional teams working across various departments or locations. When tasks or dependencies between teams are poorly defined, bottlenecks arise, as one team’s progress often relies on the timely output of another. Failing to account for these interdependencies during capacity planning disrupts workflows and hinders project timelines.
Read more: What Project Interdependencies Span Your Portfolio?
Uneven Workload Distribution Among Scrum Teams
Poor capacity planning often leads to uneven workload distribution, with some team members overworked and others underutilized. Overburdened employees risk burnout and reduced productivity, while underutilized team members may feel disengaged. This imbalance affects team morale and can lead to missed sprint deadlines, ultimately impacting the project’s success.
Relying on Outdated Tools or Manual Processes
Many organizations still depend on outdated tools or manual methods for agile capacity planning. However, these tools fail to provide real-time insights or forecast resource demands and available capacity accurately. As a result, teams face last-minute resource shortages and costly hiring decisions, making it challenging to meet agile project demands effectively.
Understanding these challenges is essential to refine resource capacity planning processes for agile teams. Now, let’s move ahead to explore the key steps and strategies for ensuring agile capacity planning effectively.
How to Conduct Effective Agile Capacity Planning
As per Scrum Institute, “Scrum capacity planning reduces the likelihood of project delays by 40%.”
This statistic underscores the importance of effective capacity planning in agile environments, where resource allocation and workload balance are crucial to timely project delivery. Let’s dive into the critical steps for conducting effective agile capacity planning-
Forecast Resource Requirement for Each Sprint
Forecasting resource requirements for each sprint involves assessing the team’s capacity and understanding the scope of work that can be realistically achieved within the sprint. It includes evaluating the available time of each team member, considering their skill sets, and ensuring that the workload aligns with the sprint goals.
By accurately forecasting resource requirements, you can prevent overloading team members and reduce the risk of delays. This planning helps ensure that each sprint is achievable and that the right resources are in place.
Read more: What is Resource Forecasting? A Guide for Project Managers
Prioritize Tasks Aligned with Sprint Goals
Scrum teams should prioritize tasks based on sprint goals, business value, and dependencies. By focusing on the most critical objectives or high-value features, scrum teams ensure they’re working on what matters most. This approach not only clarifies priorities but also minimizes distractions, improving overall sprint outcomes.
Moreover, the scrum master must account for task dependencies and address them in a logical sequence. Allocating resources to tasks in order of importance ensures that no team member is overburdened. This streamlined approach leads to smoother sprint delivery and improved customer satisfaction.
Use Dependency Mapping & Keep a Backup
Next, managers must map dependencies between tasks and scrum teams to identify potential bottlenecks. By clearly visualizing how tasks rely on each other, teams can proactively address challenges before they disrupt the workflow. This approach also enables better coordination, ensuring that critical tasks are completed on time.
Furthermore, it’s essential to keep a backup plan in place for unforeseen challenges, like resource unavailability or unexpected delays. Having a contingency plan allows teams to adapt quickly without losing momentum. This proactive planning helps maintain progress, even when unexpected issues arise, ensuring the team stays on track to meet sprint goals.
Apply Appropriate Resource Optimization Techniques
Resource optimization involves maximizing the productivity of available team members while ensuring that they’re not overbooked. Techniques like resource leveling can be leveraged to adjust task start and end dates based on team availability. Additionally, smoothing techniques should be used to adjust the float tasks and redistribute the workload evenly without affecting the critical path.
In cases where tasks adjustments aren’t enough, consider adding extra resources to key tasks that might be falling behind. This prevents delays and helps meet deadlines without disrupting the overall project timeline. By making these timely adjustments, managers can optimize performance and ensure better sprint outcomes.
Read more: What is Resource Optimization? A Complete Guide to Improve Project Delivery
Use a Modern Resource Capacity Planning Tool
Adopting a modern resource capacity planning tool is essential for accurately forecasting demands across various sprints in a project. It gives real-time visibility into team capacity and workload, allowing you to identify resource shortages or surpluses quickly. These tools optimize workforce allocation and help monitor utilization in real-time.
Additionally, the modeling and simulation features enable managers to simulate various scenarios, develop efficient capacity plans, and adjust resources as needed. Moreover, such software provides advanced analytics that facilitates informed decision-making, reduces resource-related risks, and improves financial outcomes.
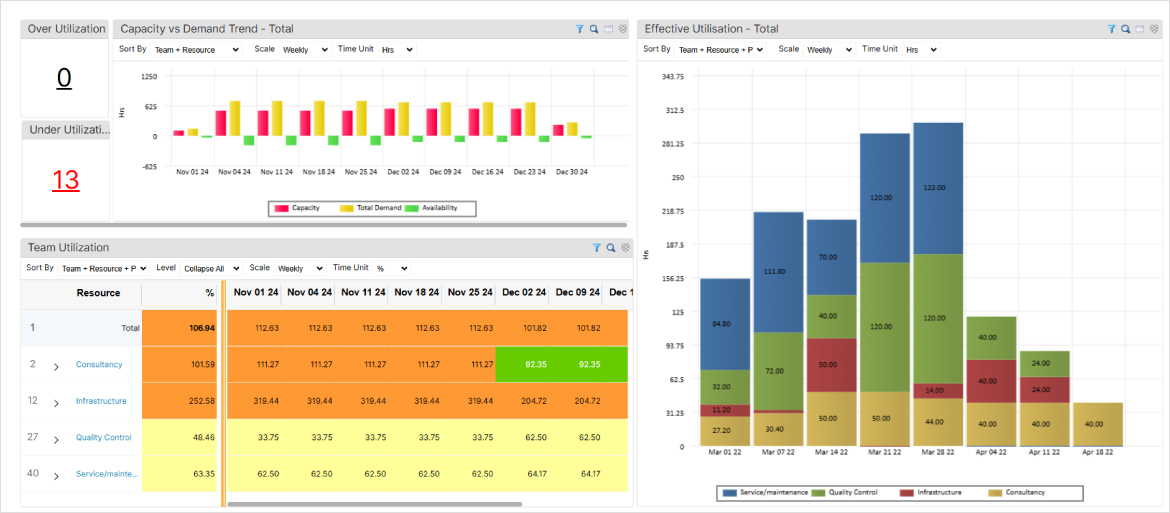
SAVIOM’s intuitive capacity planning BI dashboards enable managers to make data-driven decisions by visualizing resource utilization and performance metrics in real-time.
Conclusion
Effective agile capacity planning is essential for successful project delivery, reducing delays, and maximizing team performance. By accurately predicting resource requirements, adopting strategic approaches, and utilizing advanced resource capacity planning tools, teams can navigate the complexities of agile project management. This ensures the delivery of high-quality results on time and within budget.
So, are you ready to elevate your agile team’s productivity?
Book a 60-day customized trial with SAVIOM today!
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management











