According to a survey by IDC, ” Resource shortages within an organization can result in decreased customer satisfaction, compromised quality, and missed revenue growth targets.”
This statistic emphasizes the critical need for a robust capacity model in every organization! It enables firms to proactively anticipate, evaluate, and bridge the capacity vs. demand gaps to create an optimized and future-ready talent pool.
As a result, organizations can effectively meet both their immediate and upcoming project needs, ensure timely project initiation, optimize resource health index, improve billability, and more.
This blog aims to highlight the significance of the advanced capacity model and how it can equip organizations to build a strong framework for long-term growth and success.
To start, let’s define what a capacity model is.
What is a Capacity Model?
A capacity planning model is a strategic tool that helps businesses anticipate and evaluate the gap between upcoming project demands and existing capacity.
In case of discrepancies, managers can take suitable measures to mitigate the excesses or shortages of resources, create a competent talent pool, and ensure seamless project delivery.
Here is a scenario for better understanding:
A multinational corporation (MNC) based in Europe is managing projects at various stages, some are nearing completion, others are ongoing, and many more are in the pipeline. With two projects with a high probability of closure, managers with an efficient capacity model should start assessing the demand for the pipeline projects.
This process involves defining each project’s budget, scope, tasks, and timeline, followed by determining the type, quantity, and quality of resources required. After establishing project demands, organizations need to assess their internal talent pool, considering factors such as skills, location, cost, availability, and other relevant attributes.
Following this, managers conduct a thorough capacity vs. demand gap analysis and apply appropriate resourcing solutions, if needed. This approach enables organizations to manage global projects effectively, deliver high-quality results, improve client satisfaction, and sustain a competitive advantage in the market.
Now that we understand what a capacity model is let us explore its different types.
Types of Capacity Planning Model
Managers can select an appropriate capacity planning model based on project demand to optimize organizational capacity. The four types of capacity planning models are:
Lead Strategy
The lead strategy involves anticipating and increasing organizational capacity ahead of an expected demand. This proactive approach helps meet changing project requirements with ease, avoid last-minute resource shortages, and minimize cost overruns.
For example, a marketing firm anticipating a high-priority client campaign during the peak season may be prepared to recruit additional staff. This helps prevent last-minute resource shortfalls and ensures a smooth project lifecycle.
Lag Strategy
The lag strategy involves increasing the organizational capacity when there is a noticeable rise in demand in real-time. Although this approach helps avoid capacity wastage, minimize operational costs, etc. It may also lead to last-minute expensive hiring cycles, delayed project timelines, sub-par quality deliverables, etc.
For instance, A software development firm operates at 90% capacity with its current team, handling regular projects. They avoid hiring extra staff, increasing their capacity only when a large contract requires additional resources.
Match Strategy
Match strategy involves gradually adjusting the organizational capacity in response to changing demand. This practice ensures managers can meet demand without overloading or underutilizing the resources, enhancing employee productivity and maximizing ROI.
For example, a marketing team experiences last-minute scope changes and hires freelancers just in time to manage the additional workload, without over-utilizing resources.
Hybrid Strategy
The hybrid strategy combines critical elements of both lead and lag strategy. It involves adjusting the organizational capacity in real time while also responding to future demands. This helps minimize the risk of resource shortages or wastage, reduce costs, and optimize resource allocation.
For example, a retail company may use a lead strategy by increasing workforce and inventory in anticipation of seasonal sales. Simultaneously, it tracks daily demand and adjusts capacity per lag strategy.
Now, let’s understand how adopting an advanced capacity model benefits an organization.
Benefits of Implementing a Capacity Model in Your Firm
An efficient capacity model allows firms to evaluate current capacity, anticipate future needs, and address any demand gaps. This enables managers to secure resources proactively, minimize last-minute hiring or layoffs, reduce resourcing costs, and more.
Additionally, it provides managers with sufficient lead time to identify and deploy the best-fit global talent at competitive rates to suitable tasks. This ensures timely project initiation and progress, per predetermined timeframe and budget, without compromising quality.
Moreover, a robust capacity model allows managers to plan ahead and identify the most suitable resources based on attributes such as skills, expertise, qualifications, location, and more. This helps managers allocate the best-fit resources to projects, prevent underutilization or over-allocation, and minimize idle time.
As a result, firms can reduce instances of under- or over-utilization, enhance employee engagement, improve workforce productivity, and maintain a steady revenue stream.
As we know the benefits of a robust capacity planning model, let us dive into the steps to build one in the following section.
Read More: What is Resource Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Every Project Manager
Key Steps to Build a Capacity Model
Creating a capacity model involves careful planning and analysis to ensure an organization can meet its workload demands without exceeding resource limits. The following key steps will guide you through the process:
Take Account of Overall Resource Capacity
The first step in building a capacity model is to assess all available resources in the organization. Understanding their current workloads, utilization, and planned leaves helps managers get information about the actual capacity available to meet project demands.
Forecast Future Project Needs
Next, after estimating the overall capacity of resources, it is necessary to check the anticipated project demands. This includes considering factors such as the number and complexity of projects, the timeline, and the required resources for each project.
Read More: What is Capacity Management & How to do it Effectively?
Analyze the Demand Gaps
By comparing projected future project demands with existing resource capacity, organizations can identify gaps, such as resource shortages or surpluses. This analysis enables managers to implement corrective measures to align capacity with demand.
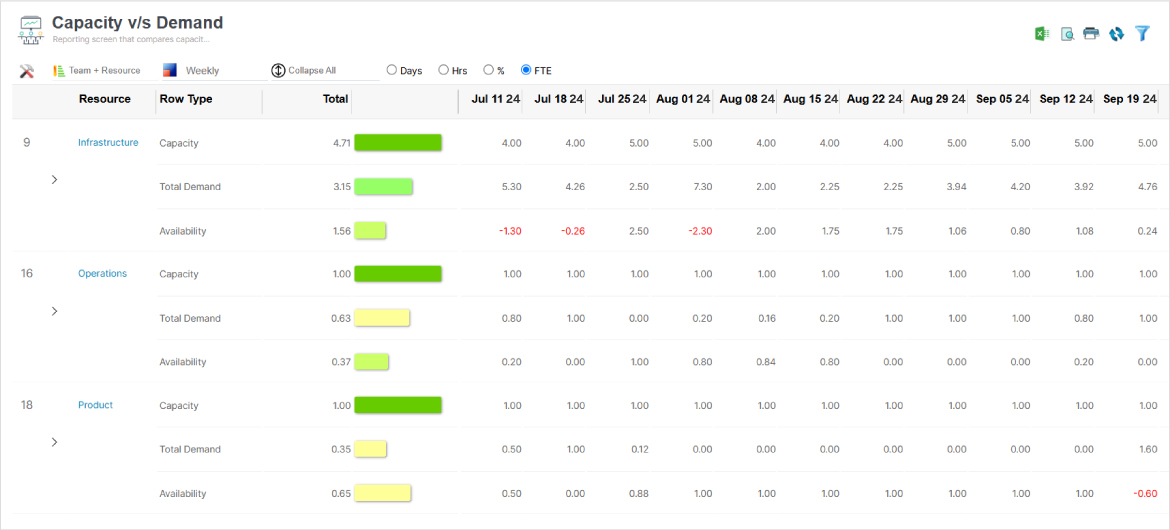
SAVIOM’s powerful Workforce Capacity vs. Demand graph helps managers take proactive measures to match capacity with future demand
Develop a Strategy to Bridge the Capacity Gaps
Lastly, resource managers can implement suitable measures to bridge demand gaps. In case of shortages, they can organize training, hiring, implement out-rotation and backfill strategies, etc. Conversely, in case of surplus, they can bring forward project timelines or sell excess capacity at a discounted rate.
Having outlined the key steps to build a capacity model, let’s explore these best practices in the next section.
Read More: What is Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Business Efficiency
Best Practices for Developing a Robust Capacity Planning Model
Below are some best practices for developing a robust capacity planning model that supports long-term business success.
Create a Buffer for High-Demand Resources
During peak demand periods, it’s crucial to have additional resources available to support critical teams. This reserve, known as a “buffer,” ensures that high-demand resources are not overburdened, preventing burnout while managing the increased workload.
Having a buffer in place also offers flexibility, allowing key team members to effortlessly take on additional tasks when required. This approach ensures that projects can scale efficiently without sacrificing quality.
Facilitate Training and Multi-Skill Building
To prepare your team for future demands, managers should evaluate current skill levels and identify any gaps. One of the most effective ways to address these gaps is by providing targeted training programs and skill-building initiatives.
Strategies like cross-training, job rotation, and mentorship can promote multi-skill development, enabling employees to take on a variety of roles. This approach enhances workforce flexibility, allowing team members to smoothly transition between tasks or roles as project demands change.
Read More: How Can Retraining/Upskilling Future-Proof Your Workforce?
Invest in a Capacity Planning Software
An advanced capacity planning tool offers demand forecasting that helps predict current and pipeline project requirements. It also provides enterprise-wide visibility into detailed resource attributes, allowing organizations to identify the most suitable people, equipment, facilities, and more for various projects.
With features like capacity vs. demand reports, the software helps forecast resource needs, pinpoint any shortages or surpluses, and make informed schedule adjustments. This enables a more balanced and efficient resource utilization, ensuring that employees are allocated optimally across projects.
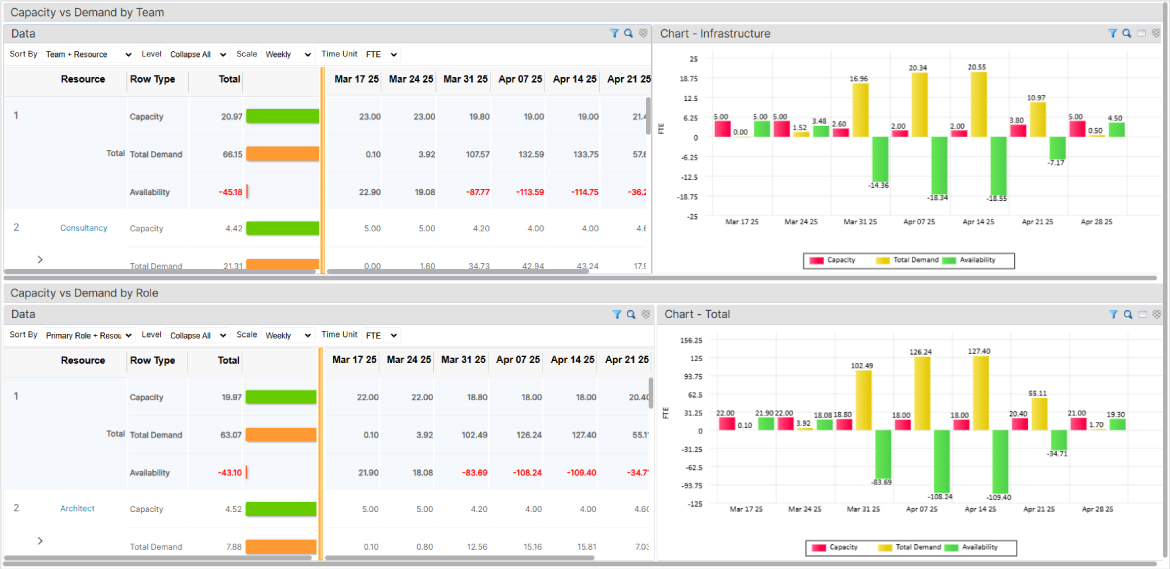
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand real-time BI insights help managers identify demand gaps, enabling quick, data-driven decisions.
Regularly Review & Adjust the Model
To maintain an optimized workforce, it’s crucial to regularly review and adjust the capacity model. This ongoing process involves assessing the framework to ensure it meets both current business needs and future demands.
In addition, integrating stakeholder feedback and making adjustments to the model ensures that resources are effectively aligned with the organization’s changing needs.
Build an On-demand Contingent Workforce
A contingent workforce is a pool of resources hired on a temporary basis to complete specific long-term or short-term projects. This includes temporary staff, contract workers, and freelancers who are brought in to provide specialized skills. They help fill demand gaps without the long-term financial commitment associated with full-time employees.
Hiring an on-demand contingent workforce enables organizations to quickly scale teams in response to project fluctuations and market demands. This flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and increased agility allow organizations to adapt swiftly and deliver projects successfully.
Develop a Backup Plan for Critical Roles
To ensure operational stability, create both short-term and long-term backup plans for critical roles. Short-term plans cover unforeseen absences, while long-term succession planning guarantees business continuity during transitions such as retirements or promotions.
Therefore, firms should identify key roles within the organization and offer focused training to potential backups. This ensures that qualified individuals are always ready to step in, reducing disruptions and ensuring smooth operations.
Read More: What is Workforce Planning, and How to Master it for Business Efficiency?
Final Thoughts
Creating a strong capacity planning model is crucial for organizations to meet evolving project demands, manage resources efficiently, reduce risks, and ensure successful project delivery. It also enables companies to scale operations effectively, improve resource utilization, and achieve long-term success in a dynamic business landscape.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management











