In today’s volatile market, most businesses encounter one of the following two situations;
Scenario 1: They have excess workforce capacity but insufficient project demands, negatively impacting the bottom line.
Scenario 2: They experience a sudden increase in project demands, but insufficient resource capacity results in missed opportunities.
Both the above scenarios jeopardize business reputation and profitability.
So, to improve business efficiency amid market uncertainty, it is crucial to proactively bridge gaps between resource capacity and demand. By accurately assessing current and future work requirements, companies can ensure they are well-prepared to meet project demands without over or underutilizing resources.
In this blog, we’ll explore key concepts and techniques for measuring resource capacity and demand and some best practices to maintain the balance in your operations.
What is Resource Capacity?
Resource capacity refers to the maximum amount of work, task, or project that can be accomplished by a particular resource over a specified period of time.
Resource capacity can be measured in various units such as hours, FTE (Full Time Equivalent), person, days, etc.
How to Measure Resource Capacity?
Resource capacity is measured by the timeline and availability of
- Full-time and part-time employees
- Permanent employees and contractors
- Employees hired and joining on a specific date
- Employees leaving the business by specific dates
The formula for calculating resource capacity is:
Resource Capacity =
This formula calculates weekly capacity by multiplying daily working hours by the number of working days. It provides a straightforward measure of available work hours for resource planning and allocation.
Now, let’s take an example –
Suppose a company has a standard policy of working 8 hours per day and 5 days per week for a full-time employee. To calculate weekly capacity for a full-time employee, the company would use:
- Working Hours Per Day = 8
- Working Days Per Week = 5
When these numbers are put into the formula:
Resource Capacity = 8 × 5 = 40
This equals one Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) or five person-days for a full-time employee.
To calculate the weekly capacity of a part-time employee working 5 hours per day, 3 days per week, the company would use:
- Working Hours Per Day = 5
- Working Days Per Week = 3
The weekly capacity will be:
Resource Capacity = 5 × 3 = 15
This equals 15 hours/40 hours = 0.3 FTE, approximately 1.875 person-days per week.
Now that we know the basics, let’s understand the various techniques for measuring resource capacity.
Different Techniques for Estimating Resource Capacity
Organizations can utilize various techniques to measure resource capacity accurately. Given below are three commonly used methods:
Historical Data Analysis:
This technique involves analyzing past project data, including resource allocation, timelines, and outcomes. By examining historical trends, organizations can identify patterns, estimate resource capacity, and determine potential constraints.
Workload Analysis:
This method assesses the workload of resources or teams by evaluating task volume, complexity, and duration. It requires a thorough understanding of project requirements, task dependencies, and workforce capabilities to estimate capacity.
Expert Judgment:
Expert judgment uses insights from experienced individuals or teams familiar with the specific industry. These experts provide subjective assessments of resource capabilities, workload distribution, and constraints based on their expertise.
Each of these techniques has its strengths and limitations. Organizations can use a combination of these methods for a more comprehensive view of resource capacity.
What is Resource Demand?
Resource demand refers to the number of resources needed to complete a particular task, project, or operation based on its scope and objectives in a given time frame.
The unit of demand for resources is measured in terms of hours, Full-Time Equivalent (FTE), person days, etc.
How to Measure Resource Demand?
Resource demand is measured by the resources needed for different activities over a specified timeline. It typically includes:
- Project-related tasks
- BAU, admin, and support activities
- Operational activities
The formula for calculating resource demand is:
Resource Demand =
Full-Time Resource Capacity
This formula calculates the capacity needed to meet the resource demand based on the available full-time hours.
Let’s look into an example:
If a company has a full-time working hours policy of 8 hours per day and five days per week, it totals 40 hours per week.
If an employee is allocated to a project for 48 hours per week, the corresponding resource demand will be 48 hours per week.
To calculate the resource demand, the company would use:
- Resource Hours Needed for the Project = 48
- Full-Time Resource Capacity = 40
The resource demand will be:
Resource Demand = 48/40 = 1.2 FTE
It is equivalent to 1.2 FTE or six person-days per week.
Now that we have covered how to measure resource demand, let’s explore the different demand forecasting methods.
Read More: What is Resource Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Every Project Manager
Methods for Forecasting Resource Demand
Organizations can use a combination of statistical and qualitative forecasting techniques to estimate resource demand accurately. Let’s explore each of these methods:
Statistical Forecasting Techniques
Statistical forecasting techniques rely on historical data and mathematical models to predict future resource demand. Some commonly used statistical forecasting methods include:
- Time Series Analysis:
This method examines past data to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. It applies statistical models such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving averages (ARIMA) to forecast resource demand.
- Regression Analysis:
Regression analysis explores the relationship between resource demand and independent variables like sales volume, customer base, or market conditions. It predicts future resource needs by analyzing how these factors influence demand.
- Forecasting Models:
Organizations can utilize specific forecasting models designed for resource demand, such as the Holt-Winters method for time series forecasting or the Bass diffusion model for new product adoption forecasts.
Qualitative Forecasting Approaches
Qualitative forecasting approaches rely on expert opinions, market research, and subjective assessments to estimate resource demand. Some qualitative forecasting methods include:
- Expert Opinion:
This involves gathering insights from knowledgeable and expert professionals like HR, managers, department heads, and industry specialists. Their opinions provide valuable insights into factors that impact resource demand, such as industry trends, market conditions, and changes in business strategy.
- Scenario Planning:
Scenario planning involves developing and exploring multiple hypothetical scenarios that could impact resource demand. These scenarios take into account various factors, such as changes in technology, industry regulations, market volatility, and organizational growth or contraction.
- Delphi Method:
The Delphi method is a structured forecasting approach that involves collecting input from a panel of experts through a series of questionnaires and iterative rounds of feedback. The iterative process allows for convergence on a consensus-based forecast, thus reducing biases and fostering a wide range of perspectives.
- Qualitative Market Research:
Qualitative market research techniques, such as focus groups, interviews, and surveys, can be deployed to gather insights from stakeholders within the organization. These methods can provide valuable information about the future needs and expectations of the workforce.
By combining statistical forecasting techniques with qualitative approaches, organizations can obtain a more comprehensive understanding of resource demand.
Read more: Resource Forecasting Guide for Project Managers
Now that we thoroughly understand the basics, let’s understand how to measure resource capacity and demand and address the gaps precisely.
Importance of Measuring Resource Capacity and Demand
Evaluating resource capacity and demand involves assessing and aligning the organization’s staffing levels with the upcoming demands to create a competent resource pool before the project’s onset.
This helps avoid unforeseen resource shortages, minimizes last-minute hiring/firing cycles, reduces resourcing costs, etc. Additionally, the capacity v. demand analysis enables businesses to match the staff availability with pipeline project requirements accurately and avoid sub-optimal resource utilization.
This, in turn, leads to enhanced workforce productivity, quality project delivery, and improved overall billability.
Now, to achieve these benefits, it is crucial to understand how to measure resource capacity vs. demand. Read on.
How to Measure Resource Capacity vs. Demand?
Here’s a streamlined approach to calculating the resource capacity vs. demand gap:
Calculate the Resource Capacity within the Organization
The first step in analyzing the capacity vs. demand gap is understanding the organization’s resource capacity. Managers should have an overview of crucial resource metrics, such as skill sets, competencies, experience, availability, and team dynamics, like departures and new hires.
It is also essential to account for factors like employee time off, planned leaves, public holidays, and operational constraints, such as maintenance schedules or peak workload periods. This ensures an accurate view of the organization’s overall resource capacity.
Read more: What is Capacity Management & How to do it Effectively?
Forecast the Resource Demand for Pipeline Projects
This involves analyzing upcoming requirements to predict the type and quantity of resources needed. Start by identifying the scope, tasks, and timelines of future projects. Then, estimate the effort required for each task, including hours, skill levels, and specific resources.
Next, consider factors like project interdependencies, complexity, and deadlines that may influence resource demand. Managers can also use historical data and expert judgment to create forecasts. This proactive approach ensures projects are adequately staffed and bottlenecks are identified before delays occur.
Perform a Capacity vs. Demand Gap Analysis
Managers can perform a demand gap analysis to determine if there is a resource surplus or shortage. This involves comparing anticipated resource needs like employee numbers, required skill sets, competencies, and availability against the current workforce capability.
For instance, if a specific skill set vital for the upcoming project does not exist within the organization, managers can take early action to ensure the project starts on time. This gap analysis helps identify and address potential capacity planning bottlenecks in advance and guarantees seamless project execution.
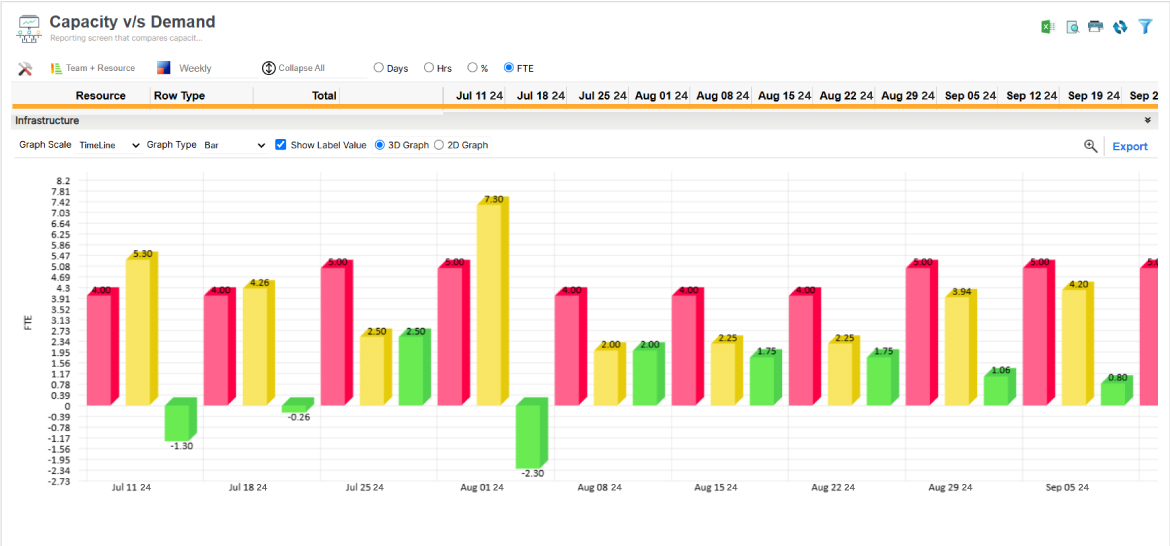
SAVIOM’s advanced Capacity vs. Demand graph enables managers to quickly identify resource excesses/shortages with minimal effort.
Create a Plan to Bridge the Gap
Once managers identify a resource excess or shortage, they can create a plan to address the gap. For instance, in case of skill shortages, firms can organize training and upskilling programs, implement out-rotation and backfill strategies, or recruit a permanent or contingent workforce based on project needs.
Conversely, organizations with a resource surplus can expedite project timelines or sell extra capacity at a discounted rate. This proactive approach ensures that competent resources are aligned with organizational goals, ensuring better resource utilization and productivity.
Read More: How Can Retraining/Upskilling Future-Proof Your Workforce?
Review & Update the Capacity Plan Regularly
Capacity planning is an ongoing process, so it is essential to regularly review and update the plan to keep the workforce optimized. This includes adjusting to changing priorities, identifying skill gaps, and resolving resourcing challenges to maintain a balanced and efficient team.
By keeping the capacity plan up-to-date, organizations can adapt to evolving needs, future-proof their operations, and maintain efficiency. Regular updates are crucial for agile and comprehensive resource management, allowing businesses to stay prepared for future challenges.
Now, let’s explore some best practices to help your organization anticipate and meet evolving resource demands.
Best Practices for Calculating Resource Capacity and Demand
Here’s how you can optimize resource capacity and demand calculations to enhance project efficiency and meet organizational goals.
Centralize All Resource-Related Information
To accurately determine the capacity vs. demand gap, consolidate and maintain all resource-related data, such as skills, availability, and utilization, into a single platform. This approach breaks down silos of resource information, thereby minimizing data duplication, promoting transparency, and enabling more accurate capacity assessments.
Analyze Historical Data for Accurate Forecasting
Reviewing past data helps forecast resource needs more accurately by spotting patterns in demand and capacity, offering a clear picture of recurring needs. With these insights, managers can better plan staffing levels, avoid shortages or surpluses, and keep projects on track.
Create Contingency Plans for Unexpected Changes
Develop a contingency plan to manage unexpected changes in resource capacity and demand. Identify potential risks like sudden project scope changes or absences and establish backup plans for reallocating resources or adjusting schedules. This ensures operational continuity and minimizes project disruptions.
Keep Track of Resource Schedules
Monitoring resource schedules is vital to understanding availability. By tracking resource utilization, organizations can assess capacity, allocate resources effectively, and prevent over/under-allocation. Further, it ensures that resources are properly aligned with timelines, boosting productivity and project success.
Read more: How to Track Resource Utilization?
Foster Effective Communication & Collaboration
Facilitating transparent communication among executives, managers, and stakeholders during resource capacity planning ensures everyone stays informed of departmental needs. Additionally, it aligns team priorities and objectives, prevents misunderstandings, and enables timely adjustments to changing priorities.
Leverage a Futuristic Resource Capacity Planning Software
An advanced capacity planning tool offers enterprise-wide visibility into detailed resource attributes to identify suitable people, equipment, facilities, etc., for various projects. It also provides capacity vs. demand reports, helping managers forecast resource needs, identify gaps, and assist managers in adjusting schedules for balanced workforce utilization.
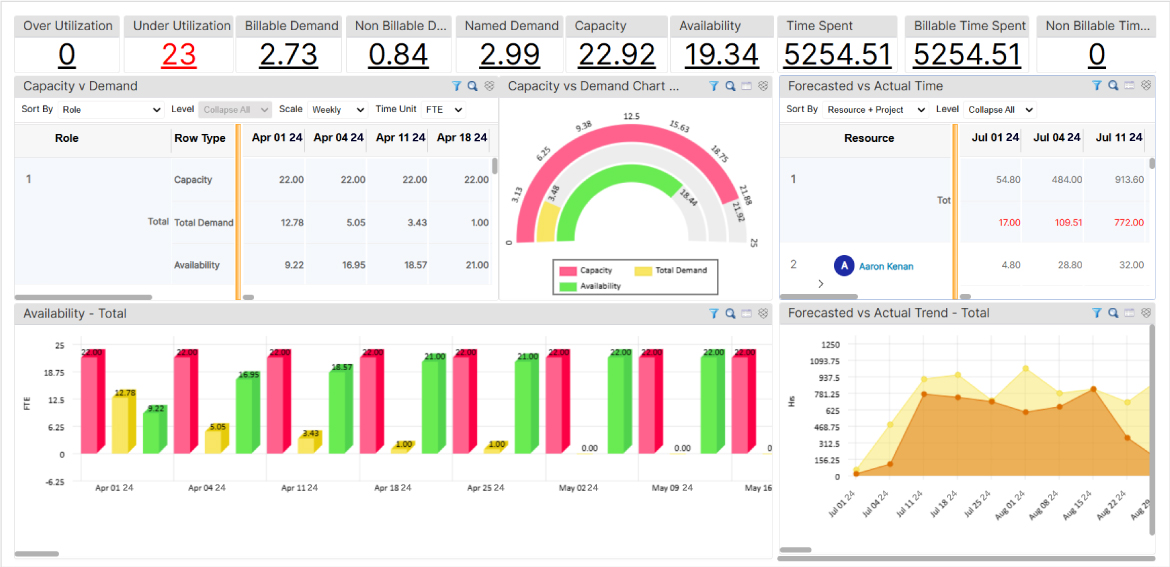
SAVIOM’s advanced Capacity vs. Demand BI dashboards help managers foresee and bridge demand gaps and keep projects on track.
Conclusion
Demand management is the holy grail of project resource management that aims to continuously match the resource demand with capacity for a productive and sustainable business operation. Thus, organizations must monitor the resource capacity and demand to efficiently allocate resources, avoid overallocation or underutilization, and meet project deadlines without compromising quality.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management












