Do you struggle to track project requirements and ensure they are properly implemented?
Is it difficult to verify that every requirement is tested without gaps or errors?
Managing project requirements is no small feat, especially when internal and external stakeholders constantly introduce new requests. Overlooking even a single requirement can derail an entire project, leading to costly delays or financial losses.
This is where the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) proves invaluable. As a vital project management tool, RTM offers a systematic approach to tracking, implementing, and validating requirements at every stage, from initiation to final delivery.
In this post, we’ll explore the definition, types, and importance of formulating an RTM to ensure project success.
What is a Requirement Traceability Matrix?
The Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a tool or a document that ensures all project requirements are linked to their origin and tracked throughout the project lifecycle. It provides a detailed mapping of requirements to deliverables, design elements, test cases, and other related artifacts. This guarantees that each requirement is implemented, tested, and verified.
Traceability Matrix is utilized throughout the different phases of the project lifecycle, such as
- Requirements Gathering: It helps establish traceability from the beginning to ensure all requirements are well-defined.
- Design Phase: The trace matrix ensures that every requirement is translated into specific design elements or specifications.
- Development Phase: It ascertains that all requirements are implemented in the development process, reducing the risk of missed functionality.
- Testing Phase: In this phase, RTM confirms that every requirement is covered by test cases, enabling defect identification and comprehensive validation.
- Implementation & Deployment: Here, RTM provides final confirmation that all requirements are met before deployment.
- Maintenance & Change Management: Here, it tracks requirement changes and their impact on existing deliverables.
Read more: Why is Change Management Important in the Timely Delivery of Projects?
Let’s have a look at the major components of the matrix:
Components of Requirement Traceability Matrix
The RTM is created according to the organizational standards and needs, but it generally includes elements such as requirement ID, baseline document reference number, bug ID, and test cases. Some of the common components include:
- Requirement ID – A unique identifier assigned to each project requirement for easy reference and tracking.
- Requirement Type – Groups or categorizes the business requirements by their nature, such as functional or non-functional.
- Requirement Description – A brief description of the requirement’s purpose and expected outcome.
- Source of Requirement – Identifies the origin of the requirement, such as a stakeholder or document.
- Priority – Indicates the urgency of the requirement in relation to the project.
- Test Case ID – A unique identifier that links the requirement to its corresponding test case for validation.
- Owner –The person or team responsible for managing and delivering the specific requirement.
- Status – The current status of the requirement, such as “pending,” “in progress” or “completed.”
Now that we understand the components of the trace matrix, let’s explore its advantages:
Benefits of Requirement Traceability Matrix in Project Management
The requirement Traceability Matrix ensures a smooth workflow and fosters successful project outcomes. Here are the key benefits it offers:
Tracks all the Requirements Throughout the Project Lifecycle
The RTM outlines all the project requirements, ensuring they are tracked from initiation through testing and delivery. This prevents any requirement from being missed and enables easy backtracking to the originating requirement in case of defects. Ultimately, requirement tracking throughout the project reduces the risk of scope creep and facilitates alignment with project objectives.
Facilitates Effective Change Management
In any project, changes are inevitable. RTM assists in assessing the implication of changes in existing requirements, design, or testing processes. When a requirement is modified, RTM enables the team to evaluate the impact of changes on a project as a whole. Thus, it ensures effectual change management and prevents project delays or budget overruns.
Improves Test Case Management
RTM links each requirement to its corresponding test cases. This linkage ensures that every requirement is appropriately tested and improves the quality of the project deliverables. Through systematically tracking test coverage, the Requirement Traceability Matrix helps identify gaps in testing, thereby preventing defects and boosting customer satisfaction.
Enhances Project Control & Accountability
The Trace Matrix defines each requirement’s status and ownership, enhancing control throughout the project lifecycle. Moreover, clear documentation of who is accountable for each requirement fosters a sense of authority among team members as they are held responsible for their contributions. This also leads to effective resource allocation and better performance monitoring.
Streamlines Communication & Collaboration
RTM provides a shared understanding of project requirements and their statuses. Thus, it is a centralized reference point and fosters better collaboration among stakeholders, developers, testers, and project managers. Additionally, the precise documentation of requirements improves communication, leading to informed and effective decision-making.
Thus, leveraging a Requirements Traceability Matrix for requirement tracing makes meeting goals and managing projects easier. Now, let’s delve deeper into its few types.
Read More: Effective Strategies for Resource Estimation in Project Management
Types of Traceability Test Matrix
There are three key types of requirement traceability matrices used in requirements tracing, as mentioned below.
Forward Traceability:
The term “forward traceability” refers to mapping requirements to test cases. This matrix is created at the start of a project to ensure that the product is progressing in the right direction. It ensures that the testing process thoroughly covers all the specified requirements.
For instance, in a software development project, a forward traceability matrix will track each feature requirement from the initial document to relevant design elements, code modules, and test cases to ensure all the features are integrated and tested correctly.
Backward or Reverse Traceability:
Backward traceability is the process of matching test cases to requirements. It enables managers to trace the source of each request and ensures that the current product is on track. The purpose is to prevent project scope creep by ensuring no unapproved codes, design components, tests, or other activities are added beyond the initial requirements.
For instance, in the F&B industry, a finished product batch is taken and traced back through the process to the materials/components/ingredients received from suppliers. This helps validate that the end product has met all the intended quality standards.
Bi-directional Traceability:
The matrix is termed bi-directional when it tracks the requirement “forward” by looking at the output of the deliverables and “backward” by examining the requirement specified in the project initiation phase. It allows teams to have complete visibility into specifications through building, testing, tracking changes, analyzing defects, etc.
For instance, In the automotive industry, bi-directional traceability would ensure that safety features, such as an airbag system, are traced forward from its requirement specification through the design, development, and testing phases. Simultaneously, the system is traced backward from the final vehicle’s functionality to the initial requirement to confirm that no additional, unapproved changes were introduced during development.
Read More: What is Risk Matrix and Why It is Important?
Now that you know the different types, let’s dive into the steps to create a requirements traceability matrix.
How to Create an Effective Traceability Matrix?
Here’s a detailed breakdown of steps to create an effective traceability matrix.
Identify all the Project Requirements
The first step to creating an RTM matrix is to collect and document every requirement for the project. For this, project managers should analyze project documentation, review regulatory requirements, and discuss with clients and stakeholders to clearly define all functional, non-functional, and technical requirements. By adequately documenting all the project requirements, project teams can establish a solid foundation for a traceability matrix.
Decide the Type of Traceability
Based on the project needs, you can decide the type of traceability matrix. If the focus is on tracking requirements to deliverables, then Forward Traceability can be used. If the goal is to validate that the final deliverables meet initial requirements, then Backward Traceability becomes the right choice. If it’s a complex project in which mapping requires comprehensive coverage in both directions, then bidirectional traceability becomes ideal.
Read More: Essential Project Management Tips for Beginners
Create a Traceability Matrix Template
Once you have consolidated the necessary information, you may design the template for your matrix. The Requirements Traceability Matrix has no set structure; instead, it may be tailored to the project’s needs & type. It includes columns for components such as Requirement ID, Requirement Description Priority, Test Case ID, Owner, etc. Moreover, RTM can be built and maintained using an automated tool, Excel spreadsheet, or MS Word table.
Review & Validate the Result
After designing the matrix, a review should be conducted with project stakeholders, team members, and the quality assurance team. The review process covers all requirements and maps to the test cases. It also helps identify missing requirements or duplicate entries. Additionally, validation ensures the traceability matrix is accurate and facilitates seamless project tracking.
Read More: What is Project LIfecycle and How to get it Right?
Impart Training to Team Members
This involves explaining to the team how to interpret the matrix and use it to track the progress. Project managers must provide clear instructions to the team on when and how to update information, such as by adding new test cases or changing the status. Further, they can define the roles so that every member understands their responsibility. The training aims to empower the team to use the matrix effectively, improve collaboration, and maintain consistency.
Update the Matrix Throughout the Project
The traceability matrix is a dynamic document that should be maintained throughout the project. The changes should be reflected in the traceability matrix when any requirements are added or existing ones are modified. Moreover, the matrix should show the correct status once the test cases are completed or changed. Updating the traceability matrix ensures the team is aligned with the requirements and project scope document.
Read More: How to Create an Effective Project Plan in 9 Simple Steps?
Let’s gain a clearer understanding of the Requirement Traceability Matrix with an example.
Requirement Traceability Matrix Example
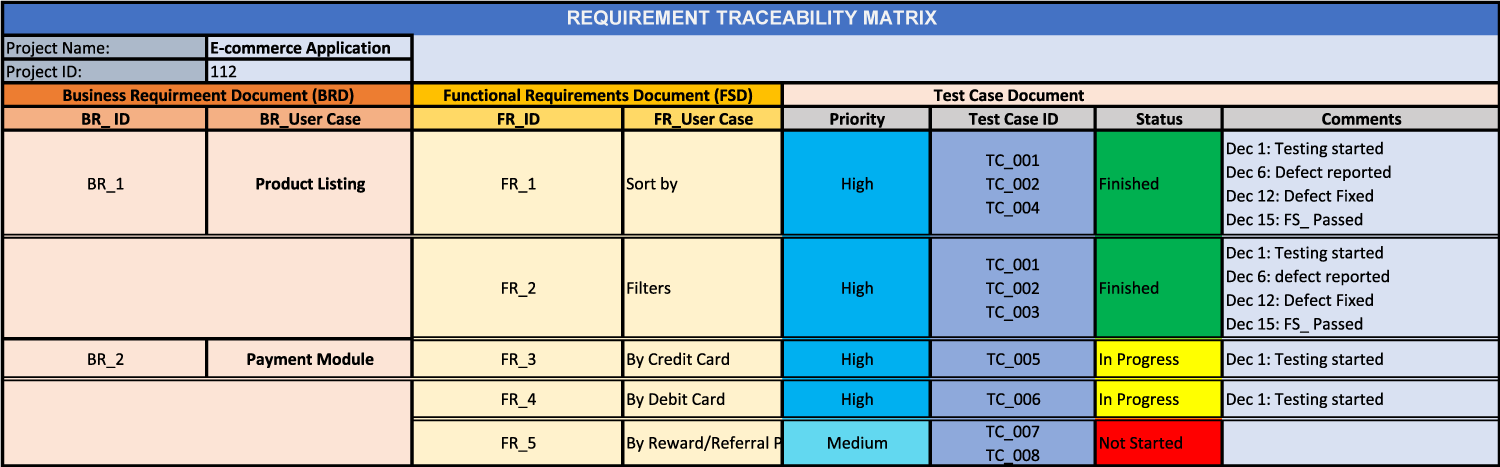
Supposedly, you got an e-commerce application project for a clothing brand. The goal of the app is to provide a seamless buying experience to the users. For that, they want two functions- One is to integrate advanced filters into the product listing, and the second is to ensure different payment gateway features.
You can define these features or goals in the RTM as given below:
- BR_1 Product listing:
It should allow users to browse through their different products with filtering features.
- BR_2 Payment Module:
Users should be able to make payments for products via Credit / Debit Card or through Reward & Referral Points.
Now, the two business requirements can have more detailed functional requirements:
BR_1 Product listing:
FR_1: Sort by
It should allow users to sort different products based on pricing, popularity, customer ratings, discounts, etc.
FR_2: Filters
It should allow end-users to implement product filtration based on size, color, brand, etc.
BR_2 Payment Module:
FR_3: By Credit Card
It should allow users to make payments with Credit Cards.
FR_4: By Debit Card
It should allow users to make payments with Debit Cards.
FR_5: By Reward/Referral Points
It should allow users to make payments by reward/referral points.
Note: In more complex systems, the traceability matrix may include references to other documents such as user requirements, risk assessments, etc.
Here is the sample template for the details mentioned above:
A. Test cases or test scenarios for each functional requirement
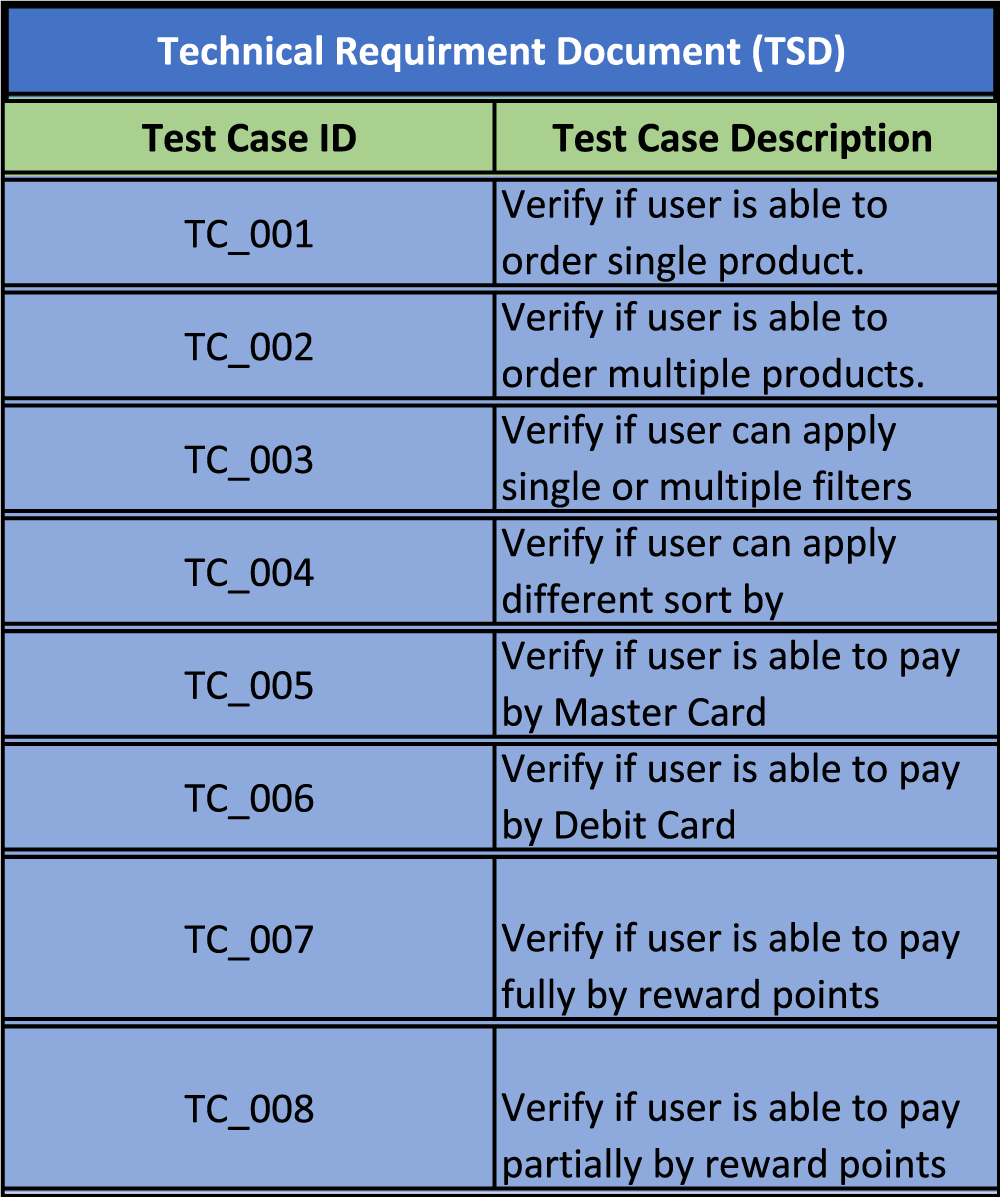
B. Requirement Traceability Matrix Template
Conclusion
The Requirements Traceability Matrix is used to track how the project progresses at each phase. It also assists project managers in making sure that deliverables meet stakeholder expectations. The information mentioned above briefly overviews the requirement traceability matrix, its significance, and how to create one.
If implemented accurately, a well-defined RTM can help a project manager avoid scope management-related issues at a later stage. As a result, it effectively helps to improve the project quality and reliability of a final product, minimizing rework and maximizing efficiency.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management












