A risk matrix can be one of the major differentiators between a well-executed project and one that faces unexpected challenges. Let’s explore a scenario to understand this:
Your organization has received a new project. As the project manager, you have defined the project charter, scope, and other necessary attributes and got your stakeholders’ approval. The project has begun and is running its due course, but suddenly, your critical resource takes unplanned leave indefinitely due to unavoidable personal reasons. Without a contingency plan in place, your project’s deadline is delayed.
Moreover, you must resort to last-minute hiring, which may lead to cost escalations and compromise the quality. In short, the risk of unplanned absenteeism translates into an issue that could derail your project. If only you had proactively assessed such risks and prepared a backup strategy, you would be better equipped to secure the project’s success. This is precisely what a risk matrix helps you do.
A risk matrix enables you to identify and assess all the risks involved and the severity of their impact on the project. With its help, you can form the best mitigation plan and control your project’s fate.
This blog takes you through concepts like what is a risk matrix, its advantages, and how to create it.
Let’s begin with the definition.
What is a Risk Assessment Matrix?
A risk matrix is a virtual representation of risks and their impact on projects. It is essentially a grid where the left side (X-axis) represents a risk’s probability, while the top (Y-axis) represents its impact. We have included a visual representation in the later section of the article for better understanding.
While the probability is generally visualized in terms of its likelihood, you can also show it in terms of percentage ranges. If a risk occurs, its impact on a project shows its severity level. Furthermore, the priority of risk increases in proportion to its likelihood and severity in the risk matrix.
Some organizations even introduce a third axis to denote the “probability of consequence,” which depicts the likelihood of a consequence once a risk occurs. This way, the risk matrix becomes a risk cube (3-D representation of risks).
Having explored the concept of a risk matrix, it is essential to differentiate between risks and issues to understand their unique roles in project management.
Risks vs. Issues
Risks are unexpected events or conditions that haven’t occurred yet but can adversely affect a project. Since each risk has a certain probability of occurrence, a project manager should assess its impact and form a contingency plan beforehand.
Issues, on the other hand, are the events that have already occurred. If risks are not mitigated proactively, they become issues and lead to significant roadblocks in project execution. These issues need urgent attention and effective control measures.
Given the differences between risks and issues, let’s read about the risks involved in a project.
Types of Risks in Project Management
No project is absolutely risk-free. However, risks are actionable as long as they don’t turn into issues. Moreover, though the exact nature of risks can vary project-wise and industry-wise, you can segregate them broadly into nine common categories, as shown below.
- Technical Risks
These risks are associated with the technology implemented during the project’s course. They can be glitches related to the software, hardware, storage, data security, etc., in your project. Failure to manage these risks may result in security breaches, system failures, increased maintenance costs, extended downtime, and more.
- Cost & Schedule Risks
Cost risk is the possibility of a project exceeding its pre-defined budget due to inaccurate estimation or unanticipated expenses. On the other hand, schedule risks happen when projects are delayed or exceed their stipulated deadline due to factors such as poor planning, resource unavailability, supply chain disruptions, etc. These risks can lead to budget escalations and project delays.
Read More: 5 Ways to Reduce Project Management Costs
- Performance Risks
Performance risks occur when a project fails to deliver the expected results, even when it meets deadlines. They arise from misaligned expectations, inadequate execution, or unforeseen challenges like sudden resource unavailability or market changes. If left unresolved, they can lead to cost or schedule overruns, affecting overall project outcomes.
- Operational Risks
Operational risks arise from obstacles in the daily activities of a project, such as procurement, production, or distribution. They can happen due to untrained staff, inefficient processes, system failures, or external events like supply chain disruptions, power outages, or new legal regulations. Operational risks can bring the project to a grinding halt and even lead to its failure, if not resolved promptly.
Read More: Operational Efficiency: What is it, and How to Maximize & Boost ROI?
- Strategic & Governance Risks
Strategic risks occur when wrong business decisions negatively impact project workflows and performance. Such risks arise due to improper implementation of business initiatives or inadequate responses to competition and environmental changes. Whereas governance risks pertain to shortcomings in internal policies or frameworks that guide a project. These risks may occur due to insufficient monitoring, unclear responsibilities, or failure to adhere to regulatory standards.
- Market Risks
Market risks refer to uncertainties arising from dynamic changes in the external operating environment. Common causes include demand fluctuations, hypercompetition, economic instability, and political climate. These risks are difficult to predict and manage, as unpredictable external forces influence them beyond a project manager’s control.
Read More: Beat Market Volatility With Efficient Resource Capacity Planning
- Legal & Environmental Risks
Legal risks arise from the failure to meet necessary law or contractual obligations. These risks may involve legal disputes or non-compliance with industry requirements. Environmental risks are potential hazards caused by external factors, such as extreme weather conditions or natural disasters. These risks can disrupt timelines and resource availability, eventually derailing the project.
- Reputational Risks
Reputational risks emerge when a project’s failure negatively affects the organization’s public image. These risks can stem from unethical behavior, poor crisis management, or public backlash. Reputational risks can lead to loss of trust, customer dissatisfaction, and long-term damage to the company’s credibility.
- External Risks
External risks are the ones that are outside an organization’s direct control but have the potential to disrupt the project’s progress. These can be related to fluctuating demands, market volatility, compliance issues with the government, etc. Such risks can arise unexpectedly and vary across industries.
Read More: What Are Resource Risks in Project Management & How to Mitigate Them?
Below is an example of a risk matrix in detail for better understanding.
Risk Matrix Example
To understand the concept of the risk matrix better, let’s consider an example here.
A construction firm takes up a new project – building a shopping mall. The firm analyzes all the aspects, understands the requirements, and comes up with the list of risks below. Against each risk, it mentions its probability of occurrence and the level of impact.
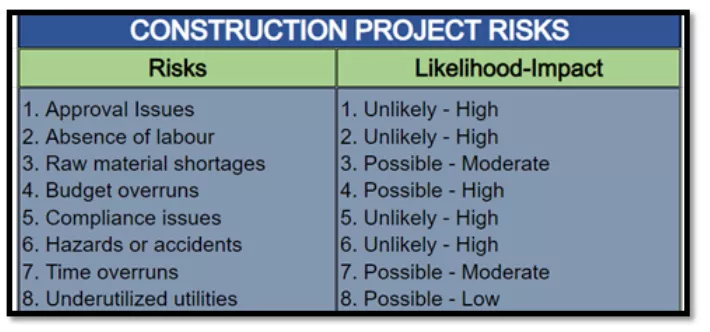
The risk matrix helps categorize risks based on probability and severity of impact.
In the next step, the project manager creates a 2×3 risk matrix. The X-axis shows two probability levels, unlikely and possible, whereas the Y-axis represents the impact levels a risk can have on the project.
Note – To keep the example simple and comprehensible, the probability and severity levels of risks have been kept to a minimum. However, real-life construction projects may use a more detailed 5×5 risk matrix or larger.
Here is the final risk matrix the construction project manager creates.
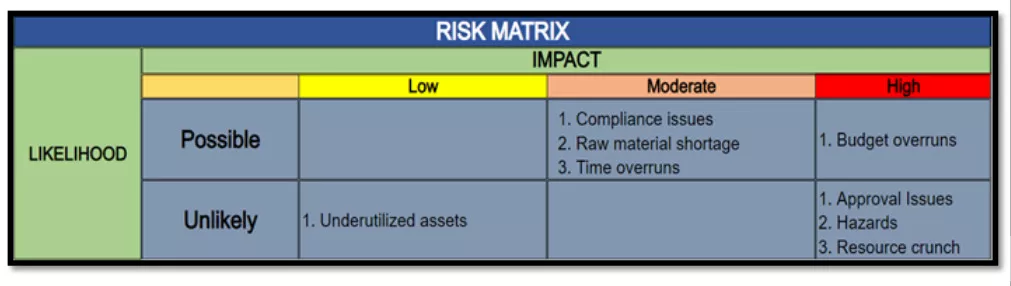 The risk matrix helps visualize and evaluate the likelihood and impact of potential risks in a project.
The risk matrix helps visualize and evaluate the likelihood and impact of potential risks in a project.
By assigning numbers to probability and impact levels in increasing order, the project manager can quantify the risks as follows:
Likelihood: Unlikely = 1 and Possible = 2
Impact level: Low = 1, Moderate = 2, and High = 3,
You can give a numerical value to each risk using this. The higher the number, the more critical the risk is. For example, “budget overruns” have a high risk rate on both probability and impact scales.
To calculate the numerical value of the risk, multiply its likelihood and impact level scale, which is:
Likelihood: Possible = 2 Impact: High = 3
Therefore,
Risk Value = 2 (probability level) x 3 (impact level) = 6
In this way, the PM can calculate the risk rates for other risks. So, the risk value for approval issues, hazards, and resource crunch will be 3 (1 x 3). Consequently, these risks can be considered “medium priority” risks. On the other hand, the risk of “underutilized assets” falls at the lowest end of both scales. Therefore, it is a low-priority risk with a 1 (1×1) value.
With this risk matrix, the construction project manager can categorize all the risks into high-priority, medium-priority, and low-priority.
This visibility into risks and their segregation into different priority levels helps formulate a robust contingency plan to tackle each risk efficiently and proactively.
For risks like budget overrun, which has the highest value of 6, the project manager should first formulate an appropriate risk response, followed by others. This way, they can proactively identify and address risks and minimize their impact on the overall project.
Now that we clearly understand the risk matrix and how to calculate it, let’s explore its advantages in more detail.
Read More: What Makes a Construction Project Fail?
Benefits of a Risk Matrix in Project Management
“PMI’s research suggests that early recognition of undesirable events is a precondition for efficient risk management.”
It is imperative for a project manager to foresee risks, be ready with a contingency plan to mitigate them and keep the project on track. The following section explains how it benefits the project management landscape:
Helps Prioritize Risks Involved Based on the Severity
A risk matrix gives managers a complete overview of all the project-related risks and allows them to assess each carefully. This comprehensive analysis of risk likelihood and impact facilitates efficient prioritization in a multiple-risk scenario. It further helps categorize risks into high, medium, and low-priority and gauge the preparation needed to tackle them.
Enables Managers to Devise Risk Management Strategies in Advance
With complete visibility of risks, the project manager can analyze their severity. Then, they can collaborate with the team to brainstorm and determine effective measures to manage them proactively. This way, a project manager can have an effective contingency plan ready to handle the risks that may surface during the project’s course. Furthermore, it helps prevent risks from turning into significant roadblocks and keeps the project from derailing or failing.
Read More: Enterprise Risk Management Framework: 8 Core Components
Ensures Timely Delivery of Projects by Eliminating Bottlenecks
A visual representation of risks helps project managers understand their potential for materializing and the hindrances they can cause. The grid format allows easy categorization and enables proactive planning to avoid delays and ensure timely project completion. For instance, a construction project manager concerned about the timely raw material supply could proactively look for alternative suppliers to prevent hurdles and delays in the future.
Standardizes Risk Evaluation Protocol Across the Enterprise
Risks can vary from one project to another. As a result, the risk matrix cannot be precisely the same for two projects. However, defining the standard criteria for risk evaluation in a project, i.e., implementing a risk matrix, can help improve efficiency. Moreover, this systematic protocol keeps everyone on the same page and makes it easy for stakeholders to evaluate and approve action plans.
Ascertains Regulation of Resource Health Index
Resources are crucial for project success, and so is understanding the associated risks. It involves reduced employee productivity, poor engagement, unplanned leave, burnout, sudden attrition, etc. Thus, addressing them on time can secure your project’s budget and timeline while keeping the resource health index in check. Additionally, project managers can plan for backup resources to combat unplanned absences of critical employees.
Prevents Potential Scope Creep and Controls the Project’s Lifecycle
Sometimes, risks can affect the entire project lifecycle if they materialize. However, a risk matrix enables a project manager to determine risks that could result in scope change. It also helps find the extent to which a scope change is manageable. The project manager can then devise a change management plan to mitigate risks, minimize scope change, and prevent it from becoming scope creep.
Read More: What is Scope Creep, and How to Avoid it in Project Management?
Provides a Real-Time View of the Evolving Risk Environment
A risk matrix offers a real-time view of the evolving risk landscape by continuously tracking their likelihood and impact. It helps project managers identify emerging and recurring risks, enabling them to adjust strategies as needed. It also allows managers to stay forewarned, handle abrupt challenges, and maintain project momentum.
After discussing the benefits of a risk assessment matrix, let’s understand its drawbacks.
Limitations of Risk Matrix
Despite its usefulness, the risk matrix has certain limitations that affect its accuracy and applicability. One major barrier is that assessment of the likelihood and impact of risks is often subjective, which may lead to unreliable results and poor decision-making.
Another prominent challenge is the oversimplification of complex risks by reducing them to static dimensions of likelihood and impact. This proves to be problematic when dealing with risks that have multiple interconnected factors or dependencies.
For instance, complex risks such as cyber threats, geopolitical events, or supply chain disruptions may involve a series of dynamic factors that cannot be effectively categorized in a static matrix.
Moreover, this approach does not account for time frames as it treats short-term and long-term risks on the same scale. This can lead to a failure to prioritize risks based on their urgency or an inappropriate allocation of resources for addressing them.
Besides, the matrix’s fixed nature often fails to capture the dynamic and evolving nature of risks such as emerging technologies, market fluctuations, or regulatory changes, potentially leaving organizations unprepared for addressing challenges.
Having explored the benefits and limitations, let’s dive into the process involved in creating a risk assessment matrix.
Read More: Top 12 IT Project Risks: Effective Ways to Mitigate Them
How to Create a Risk Matrix?
Below are the nine primary steps to create an effective risk matrix for your project.
Define the Purpose of the Matrix
In the first step, it’s important to define the purpose of the risk matrix. This involves understanding why you need it and how it will help the project. A clear purpose guides the identification and assessment of risks and ensures the matrix aligns with the project’s objectives.
Moreover, identifying the specific goals of the matrix helps determine the factors to be included, such as risk likelihood and impact. This step sets the foundation for effective risk management by ensuring the matrix focuses on addressing the most critical risks.
Customize the Matrix According to Your Project
The second step is to customize the matrix, as the type and size of a risk matrix are unique to the project’s nature and requirements. Based on these factors, you can determine the likelihood and severity levels of the risk. This approach helps to tailor the size and add other dimensions, such as the probability of risk and range the severity from very low to very high instead of just low to high.
For instance, an IT project risk matrix is generally 5 x 5. It is because the risks are multi-faceted and have five levels ranging from “Very Low” to “Very High” in terms of likelihood and severity. Customizing the matrix in this way ensures a comprehensive assessment of IT risks.
Identify the Potential Risks That Could Surface in the Project
Once you customize the risk matrix, the next step is the identification of risks. It is imperative to diligently assess the project’s attributes and tasks involved, including the industry it belongs to and more. Based on that analysis, the risk that can surface can be documented.
Additionally, you can refer to past projects of the same nature, find the risks that surfaced previously, and add them. Moreover, the lessons learned reports can help look into the mitigation strategies that were used and improve the current risk management plan.
Analyze the Likelihood of Risks and Their Impact on the Project’s Progress
The next step is to assess the probability of risks and their potential impact on a project. In this, you can use the predefined risk evaluation criteria to determine each risk’s likelihood and impact. You can also refer to previous project closure reports, stakeholders’ experience, and examples from your industry for more accurate analysis.
The probability of risk can be rated between 1 to 5, and the severity of the risk’s consequences can also be rated as low, medium, or high. You can also give a numerical value to your risk as well by multiplying the severity and likelihood. For instance, in a 5 x 5 matrix, the risk that is very likely and has a very high impact on the project would rank as 25.
Read More: Requirement Traceability Matrix: Definition, Types & Its Significance in Project Management
Create a Risk Matrix Template
Following that, project managers must create a risk matrix template. They must determine the number of rows and columns the matrix will have to show likelihood and impact intervals. Each scale should be labeled with clear intervals, such as numerical values (1 – 5) or percentages (0% – 100%).
These intervals can then be used to populate the grid with the identified risks based on their probability and effect. Furthermore, the template should be customized based on the project’s requirements to assess potential threats efficiently. For example, a 3×3 or 4×4 matrix might suit the project, depending upon its complexity.
Prioritize the Risks Based on Criticality and Probability
In this step, project managers must segregate the risks based on priority. For that, they must assign each risk a rank and prioritize them in 3-4 categories, such as critical, major, moderate, minor, etc. In addition, they can use numerical values to further refine the ranking and identify the most critical risks.
Once risks are ranked, managers can evaluate their potential impact on project goals. Moreover, they can focus on the risks that could significantly disrupt timelines, budgets, or deliverables. This approach helps address the most pressing challenges proactively so that they don’t turn into issues.
Read More: What Are Resource Risks in Project Management & How to Mitigate Them?
Prepare a Risk Mitigation Plan
After identifying and prioritizing risks, the next step is to develop a comprehensive mitigation plan. It should clearly define the actionable steps that can be implemented quickly to minimize the impact of these risks. This can include preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of occurrence and responsive actions to manage their effects if they arise.
Further, the risk mitigation plan should include designated individuals or teams responsible for monitoring and executing mitigation strategies. This ensures everyone understands their role in managing risk. Lastly, the plan must be practical and tailored to each identified risk, with clear guidelines on addressing specific issues.
Monitor and Update the Risk Matrix Regularly
The process does not end with creating a risk matrix; it should be regularly monitored and updated to ensure its relevance. Frequently monitoring the risk matrix helps identify the strategies that are not delivering the desired results. This allows project managers to make timely adjustments to optimize the risk matrix.
Furthermore, updating the risk matrix ensures it accurately reflects the current risk landscape. It enables managers to reassess the risk profile and identify emerging threats. This way, the ongoing reassessment helps teams stay proactive in addressing potential challenges before they escalate and impede project progress.
Read More: Project Constraints: What are They, and How to Manage Them Effectively?
Now that we know how to create risk matrices, it is essential to understand the role of a resource management tool in risk mitigation.
How can a Resource Management Tool Help in Risk Mitigation?
A resource management tool helps you prevent and mitigate resource-related risks in multiple ways such as:
- It provides 360-degree visibility of resources allocated to various projects. Thus, it enables better project planning and reduces the risks of resource conflicts.
- The advanced filter lets the project managers pick the best-fit resources based on skills and competencies. This way, it prevents the allocation of over/under-skilled resources.
- It also generates data-driven, real-time business intelligence reports that provide actionable insights into metrics such as availability and utilization to help make informed decisions. These decisions prevent the risks from turning into major issues and prevent a project from veering off the track.
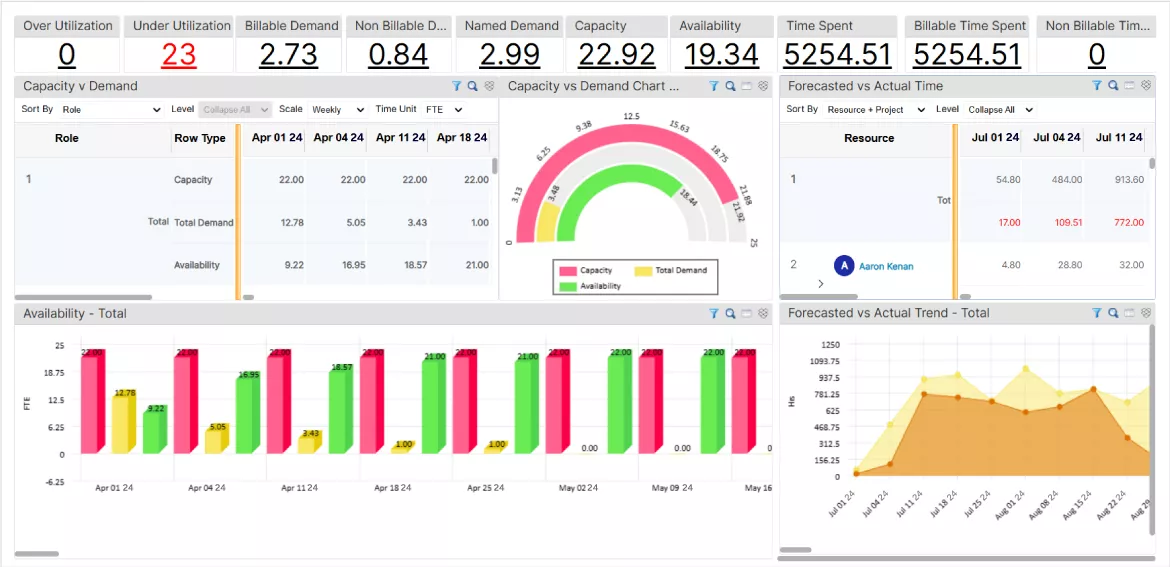
SAVIOM’s real-time BI dashboard provides in-depth insights into the utilization, availability, and capacity of every employee.
- The forecast vs. actual time report helps track time spent by resources on tasks and highlights variances from initial estimates. This allows managers to take corrective measures and keep the project on schedule.
- What-if analysis allows firms to simulate different scenarios and assess the impact of various parameters on the overall project. Accordingly, managers can optimize project planning and minimize the impact of risks.
Conclusion
It is evident that no project is risk-free, and an ideal risk mitigation plan doesn’t exist. However, the difference lies in how well you foresee and manage those risks. Hence, a risk matrix is an assessment technique that helps a project manager do that. It helps plot all the risks graphically, prioritize them, and form a risk management plan. Thus, a risk matrix can empower a project manager to make every project a success.
So, are you ready with a risk matrix for your next project?
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management






