A joint survey by KPMG, AIPM, and IPMA reveals some eye-opening statistics:
- 70% of organizations struggle to deliver projects on time.
- 64% of businesses fail to stay within the budget.
- 56% of companies cannot meet their original goals and business objectives.
- 54% of projects do not achieve stakeholder satisfaction.
These statistics emphasize the importance of identifying project constraints early on and developing a robust plan to manage them effectively. By doing so, firms can ensure the successful delivery of projects and boost profitability.
This blog will give you a comprehensive view of project constraints and their interrelations, followed by the best ways to overcome them.
But first, let’s start with the definition.
What are Project Constraints?
Project constraints are limitations that impact the success of a project. These constraints define the boundaries within which a project must be delivered. They are usually interconnected, meaning that a change in one constraint will likely affect others.
“As per the PMBOK Guide, a constraint is a limiting factor that affects the execution of a project, program, portfolio or a process.”
For example, for developing an e-commerce website, the scope might include designing five pages, adding a contact form, integrating features, etc. Expanding the scope mid-project, such as adding more pages, could affect time, cost, and resource constraints.
In 1969, Dr. Martin Barnes identified scope, time, and cost as the primary project constraints, also known as the triple constraints. With time, project managers have found other limiting factors affecting overall project performance.
The PMBOK Guide has identified and defined six project constraints that every manager must consider:
- Scope: The work as defined in the contract or charter
- Time or schedule: The deadlines imposed by the customer
- Budget or cost: The funding limits set by the sponsor
- Quality: The quality standards of the deliverables
- Resources: The availability of skilled labor
- Risks: Threats that may impact the project
Now that we understand what is a project constraint, let’s discuss the triple constraints in detail below.
The Triple Constraints of Project Management
Let’s explore the three foundational constraints of project management, commonly referred to as the triple constraints:
Scope
The scope of a project defines the specific boundaries, deliverables, and objectives that must be achieved. It outlines what is included and excluded from the project, serving as a roadmap for the team. However, poorly defined or uncontrolled scope can lead to scope creep. Therefore, maintaining a clear and agreed-upon scope plan is essential for staying on track and meeting stakeholder expectations.
Time
Time constraints dictate the project schedule, outlining when tasks should be completed. If deadlines are not managed effectively, projects can fall behind schedule, resulting in rushed work and increased stress among team members. Consequently, it may lead to missed project milestones, lower quality outcomes, and client dissatisfaction. Effective time management ensures that resources are utilized efficiently and helps meet deadlines, maintaining project momentum.
Cost
Cost constraints encompass the financial resources allocated to a project, including budgets for labor, materials, and overheads. These constraints determine how much can be spent to achieve project objectives. Moreover, they influence decisions made throughout the project lifecycle. Consequently, effective management of costs is essential to avoid budget overruns and ensure financial feasibility.
Read More: 5 Ways to Reduce Project Management Costs
After the triple constraints, it’s time to explore the other common constraints.
Other Common Project Constraints
Quality
Quality constraints focus on the standards and specifications that project deliverables must meet. It ensures that the final product satisfies customer expectations and regulatory requirements. If quality is compromised, it can lead to rework, increased costs, and loss of customer trust. Thus, a comprehensive quality management plan helps maintain standards consistently throughout the project lifecycle.
Resources
Resource constraints involve the availability and allocation of both human and non-human resources needed for project execution. Limited access to skilled personnel, equipment, or materials can hinder progress and impact project quality. Here, a suitable resource management solution can help facilitate efficient resource allocation, optimize utilization, and ensure successful delivery.
Read More: What are Resource Constraints, and How Does It Affect Project Success?
Risks
Risk constraints pertain to uncertainties and potential threats that may impact project outcomes. Failure to address these risks can lead to unforeseen issues, cost escalations, and schedule delays. Therefore, developing a comprehensive risk management plan enables teams to anticipate and mitigate risks, ensuring smoother project execution.
Technology
Technology constraints refer to limitations in the tools, platforms, or systems available for a project. These constraints can hinder project execution by restricting capabilities, requiring extra training, or causing compatibility issues. Moreover, these technical challenges can compromise project schedule and quality. Therefore, by addressing these issues proactively, teams can maintain productivity and project performance.
Sustainability
Sustainability involves integrating eco-friendly practices into project planning, design, and execution. This may limit material options, increase costs, and extend timelines due to sourcing challenges and the need for specialized expertise. However, these factors require careful consideration to balance sustainability goals with project budgets and deadlines for successful delivery.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance and regulatory requirements ensure adherence to laws, industry standards, and safety protocols. These may include local, state, and federal regulations, quality assurance standards, and environmental considerations. Failing to meet these requirements can cause delays and escalate costs. Therefore, proper integration of these regulations into project planning is necessary.
Strategic Alignment
Strategic alignment ensures that projects support organizational goals. Projects that don’t align may be deprioritized or halted, impacting resource allocation. Moreover, tight deadlines to meet strategic initiatives or market demands can compromise quality. Typically, the PMO (Project Management Office) helps assess alignment, ensuring projects contribute to the organization’s growth.
Read More: What is the Strategic Alignment of Portfolio, and Why is it Important?
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are vital to project success and the team’s well-being. Hence, risk assessments should be conducted regularly to identify potential hazards, including physical, chemical, and biological risks. Additionally, adhering to local, national, and industry safety standards is essential, and workers may require personal protective equipment.
Cultural and Ethical Constraints
Cultural and ethical constraints influence project decisions and execution. Hence, respecting cultural differences and ethical standards is crucial. Failure to consider these can lead to misunderstandings, conflicts, and reputational damage. Therefore, it is essential to integrate cultural sensitivity, adhere to ethical guidelines, and ensure inclusivity in all aspects of project planning and delivery.
Now, let’s understand how businesses can mitigate project constraints and ensure a seamless delivery.
How to Manage Project Constraints?
If you ask any experienced project manager about the most challenging part of their job, the most common response would probably be “managing project constraints throughout the project lifecycle.”
Constraints are integral to projects, but there are steps to manage them efficiently for successful delivery. Here are five effective ways to manage project constraints:
Identify the Project Constraints
Managers must identify constraints, prioritize them, and assess how they might influence the project. This understanding enables them to make informed decisions, allocate resources more effectively, and develop strategies to mitigate risks associated with these constraints.
For example, in a construction project, it is vital to identify budget and resource constraints early. This allows the project manager to prioritize critical tasks, secure the necessary resources, and allocate the budget accordingly. Doing so helps them avoid project delays due to resource shortages and fund deficits.
Categorize and Prioritize the Constraints
Once project managers have identified the constraints, they must categorize them based on criticality. They must prioritize the most critical constraints, such as scope, time, cost, and resources, followed by others, such as quality, risk, technology, etc. This categorization helps managers focus on what truly impacts project outcomes.
For example, in an IT company, the development team is building a mobile app for an important client. It is a top priority for them to adhere to the delivery date. So, the project manager focuses on launching the MVP on the scheduled date while pushing back the additional features for a later release. By focusing on the time constraint, the team can maintain project momentum and meet client expectations.
Develop Effective Risk Management Plans
A robust risk management framework involves identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing contingency plans to address them. By regularly monitoring and updating the risk management plan, managers can allocate resources (human and non-human) intelligently, minimize downtime, and prevent project failures.
For example, in construction projects, developing an effective risk management plan may involve identifying potential bottlenecks such as extreme weather conditions, procurement delays, or equipment failure. Project managers must create mitigation strategies for each risk and regularly monitor the progress. This proactive approach ensures that construction projects stay on track and within budget.
Read More: Enterprise Risk Management Framework: 8 Core Components
Monitor and Control the Constraints
Monitoring and controlling the constraints is vital to ensure that the project stays within its pre-defined parameters. For this, managers can regularly monitor the project’s progress, identify deviations, and take corrective actions to prevent escalations.
For example, project managers can regularly monitor the resource schedules to identify underutilized or overworked team members. Accordingly, they can apply optimization techniques such as resource leveling and smoothing to address the workload imbalance. This way, they can prevent unplanned absences due to burnout or disengagement.
Maintain Clear Communication Channels
Transparent communication is a critical factor in successfully managing project constraints. That’s why project managers must develop a well-defined communication plan that outlines how project updates will be shared throughout the lifecycle. It should specify the stakeholders involved, communication channels, and frequency, ensuring key information flows through the right channels to all relevant team members.
Regular updates, meetings, and open channels for feedback are essential practices that help identify issues early, facilitate quick decision-making, and maintain alignment with project objectives. By cultivating a culture of transparency, teams can build trust, enhance employee engagement, and respond to challenges more efficiently, ultimately contributing to project success.
Read More: Why Project Communication Skills are Important and How to Master Them?
In the following section, let’s learn the best practices for managing common constraints effectively.
Best Practices for Managing Project Constraints
Plan and Strategize Each Project Phase
This involves defining clear objectives, deliverables, and timelines while anticipating potential constraints such as scope, budget, and resource limitations. By breaking the project into manageable phases and establishing milestones, teams can ensure they stay on track to meet overall project goals.
Read More: What is a Project Plan & How to Create an Effective One?
Understand Each Project Constraint Clearly
Managers must understand the nature and impact of each constraint (scope, time, cost, quality, resources, and risk) on the project. In addition, assessing risks and building contingency plans help ensure successful constraint management and project execution.
Have Proper Quality Management Techniques
The deliverable’s quality must be up to the mark. For that, managers must establish quality benchmarks, implement quality assurance processes, and conduct regular audits to identify deviations early. This reduces the likelihood of rework, ensures standards are met, and enhances project stakeholder satisfaction.
Optimize Resource Allocation and Utilization
An intuitive resource management solution offers forecast vs. actual utilization reports and color-coded heatmaps to identify variances and assess over or underutilization. This way, managers can analyze root causes, take corrective actions, and apply resource optimization techniques for an equitable distribution of workloads.
Read More: What is Resource Utilization? A Complete Guide to Improve Business Efficiency
Ensure Transparent Communication between Team and Project Stakeholders
Transparent communication involves regular updates, meetings, and open channels for feedback. These essential practices help identify issues early, facilitate quick decision-making, and maintain alignment with project objectives. Through transparency, teams can build trust, enhance engagement, and respond to challenges more efficiently.
Apply Scenario Planning and Forecasting
Scenario planning and demand forecasting help manage project constraints by predicting potential challenges. The what-if analysis technique allows teams to evaluate various scenarios and select the best-fit project resource plan. On the other hand, forecasting techniques help anticipate resource needs, enabling proactive adjustments to stay on track.
Read More: What is Resource Forecasting? A Guide for Project Managers
Establish a Formal Change Management Process
A formal change management process ensures project constraints are effectively managed by providing a framework for evaluating, approving, and implementing changes. This structured approach minimizes disruptions, maintains alignment with project goals, and adjusts resources accordingly.
Adopt Flexibility and Agility in Project Planning
Adopting flexibility and agility in the project plan involves being open to adjustments in project scope, timelines, and resource allocation as needed. By embracing iterative processes and encouraging team collaboration, project managers can quickly respond to changes, mitigate risks, and ensure alignment with evolving project goals.
Read More: 10 Ways to Improve Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Use Lessons Learned to Refine Future Projects
Analyzing mistakes from past projects helps identify recurring issues and constraints. By applying these lessons learned, teams can improve planning and resource allocation. This leads to better risk management and more efficient handling of future project constraints.
Let’s understand how a project resource management tool can help managers mitigate common constraints.
How Can Project Resource Management Software Help Control Constraints?
An advanced project resource management solution can help managers identify and mitigate project constraints in the following ways.
- Provides 360-degree Visibility Across the Enterprise: The tool centralizes all project and resource data, eliminating the need for multiple spreadsheets. With a single source of truth, it provides a comprehensive view, enabling better decision-making and reducing data silos.
- Forecasts Future Project Resource Demand: Capacity planning features help forecast resource demand, providing insights into availability and upcoming project needs. This allows businesses to identify resource gaps early, ensuring timely project delivery.
- Monitors and Keeps Project Financials on Track: Advanced analytics and dashboards track cost, revenue, and profit margins. This helps managers align actual spending with forecasts, improving future estimates and increasing profitability.
- Provides Real-Time Business Intelligence Report: Configurable dashboards and real-time reports offer insights into resource performance, utilization, and project timelines. These business intelligence reports help decision-makers proactively address potential issues.
- Helps Create an Effective Resource Plan with What-If Analysis: What-if analysis enables scenario simulations to assess the impact of resource allocations. It helps prioritize projects and manage constraints, ensuring optimal ROI and efficient resource utilization.
- Streamlines Resource Allocation and Scheduling: The platform ensures the right resources are assigned to the right projects at the right time. This optimizes resource utilization, reduces overbooking, and helps in timely project delivery by matching skills and availability with project requirements.
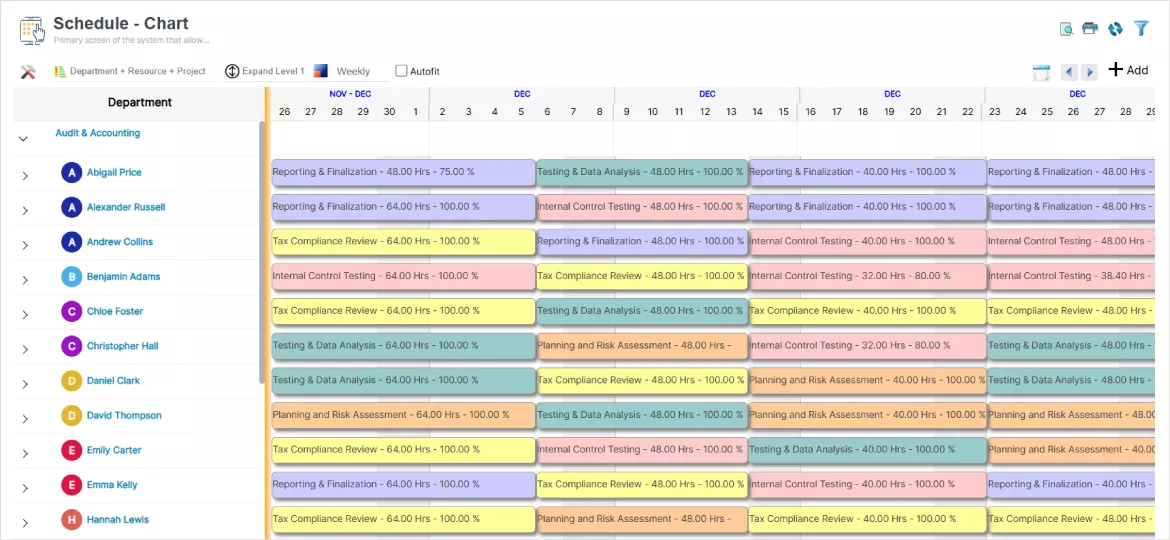
SAVIOM’s multi-dimensional scheduler enables firms to match the right resources to appropriate projects based on skills, department, cost, location, etc.
- Facilitates Real-Time Collaboration: The built-in collaboration platform streamlines communication across teams. It allows real-time sharing of updates, feedback, and files, fostering seamless collaboration and alignment between all stakeholders.
- Helps Identify Cost Variance: The forecast vs. actual cost report helps compare estimated costs with actual spending. This enables managers to identify discrepancies, adjust budgets, and improve financial accuracy in future project planning.
Conclusion
Effectively managing project constraints is crucial for successful project delivery. By identifying constraints early, applying best practices like scenario planning, and utilizing the right tools for resource management, project managers can mitigate risks and stay on track. Moreover, a clear change management process, regular monitoring, and learning from past experiences help teams adapt and optimize their approach. With these strategies, businesses can navigate project challenges and achieve successful outcomes.












