In a perfect world, finding the right skill for every job, in the required quantity and quality, is achievable. However, the reality is far from ideal, as we encounter:
- Multiple projects are frequently competing for the same talent pool
- Unplanned absences/attrition is leading to resource shortages or
- Managers frequently are engaging in costly last-minute hiring
These challenges not only hinder operational efficiency but also lead to missed opportunities, increased costs, and lower-quality deliverables. This highlights the urgent need for implementing a strong capacity planning framework.
Capacity planning is crucial for accurately predicting and aligning an organization’s current resources with changing business demands. This allows businesses to optimize workforce allocation, enhance team utilization, and reduce costs.
This guide will cover the essential concepts, benefits, and best practices to equip firms with the knowledge needed to create an effective capacity plan.
What is Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning is the process of forecasting, analyzing, and bridging the current and future demand gaps to build a robust talent pool. It involves assessing whether an organization has the necessary resources, including personnel, facilities, finances, equipment, etc., to fulfill pipeline project requirements. The primary goal is to ensure that the right resources are available at the right time, minimize last-minute hiring, and drive successful project outcomes.
Firms can employ a capacity planning formula to calculate the capacity for a given period. The formula is:
Available Capacity =
Workforce Utilization Rate
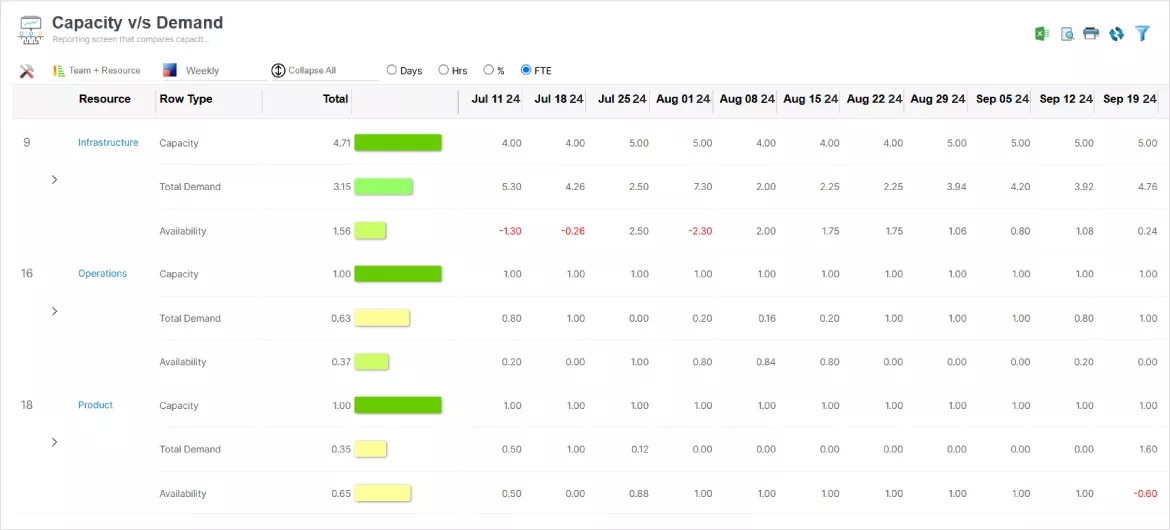
SAVIOM’s state-of-the-art Workforce Capacity vs. Demand reporting screen allows managers to visualize demand across various dimensions like location, cost, skill, etc.
Let us now understand the concept better with a capacity planning example.
Capacity Planning Example
Imagine an IT consulting firm that has three new projects in the pipeline. Based on the project demand and client commitments, the estimated workforce requirements are as follows-
- Project A – 1000 hrs.
- Project B – 800 hrs.
- Project C – 1600 hrs.
So, the total workforce demand = 1000 hrs. + 800 hrs. + 1600 hrs. = 3400 hrs.
Upon assessing the workforce availability, the firm has 20 consultants ready to take on the project.
Now,
- Weekly capacity per consultant = 8 hrs./day x 5 days/week = 40 hrs./week
- Monthly capacity per consultant = 40 hrs./week x 4 weeks/month = 160 hrs./month
Therefore,
- Total capacity of 20 consultants = 20 x 160 hrs. = 3200 hrs.
Comparing both capacity and demand,
- Expected demand – Available capacity = 3400 hrs. – 3200 hrs. = 200 hrs.
Thus, the IT firm has a capacity shortfall of 200 hours or 1.25 FTE. Accordingly, the firm can apply resourcing measures like upskilling, training, adjusting workforce schedules, or hiring temporary staff to bridge demand gaps and ensure seamless project execution.
Having understood the basics, let’s move on to various types.
Capacity Planning Types
Understanding the following three types of capacity planning is crucial for effectively meeting market and organizational demands. Here’s what each one entails –
Long-term Capacity Planning
Long-term capacity planning is a proactive approach taken by organizations to meet anticipated future capacity requirements, generally spanning several years. This method is perfect for companies looking to scale, as it assists in making decisions about investments in new technology, workforce hiring, infrastructure, and more.
Short-term Capacity Planning
Short-term capacity planning is another approach firms take to assess short-term capacity on a weekly, monthly, or quarterly basis to fulfill fluctuating demands. This involves adjusting existing staff or production schedules, reallocating workloads, changing personnel, and more.
Tactical Capacity Planning
Tactical or mid-term capacity planning involves forecasting & evaluating workforce requirements to meet evolving demands over two to five years. This involves adjusting current capacity based on seasonal fluctuations and historical trends to build a workforce ready for the future.
Next, let’s explore some KPIs that provide insight into the efficiency of capacity planning within an organization.
Read More: What is Workforce Planning, and How to Master it for Business Efficiency?
Capacity Planning KPIs
Companies focusing on capacity planning KPIs can improve their workforce efficiency, demand alignment, overall productivity, and profitability.
Below are a few crucial KPIs for businesses:
Workforce Availability
This key performance indicator tracks the amount of time the workforce is available to contribute to a project. It ensures that the right number of employees are available at the right time to meet the current/upcoming demands and enhance overall productivity. The formula to measure workforce availability is:
Workforce Availability =
(Total Booked Hours + Total Non Booked Hours )
A high workforce availability rate indicates that the team is typically accessible and prepared for the project as scheduled. In contrast, the low rate suggests that issues such as absenteeism or inadequate staffing levels need to be addressed with corrective measures.
Team Utilization Rate
This metric measures the percentage of time the team spends on billable work relative to their total available working hours. By calculating this KPI, managers can determine whether their team’s capacity is being utilized optimally and if it aligns with the organization’s productivity goals, without overloading them. The formula is:
Team Utilization Rate =
A high utilization rate suggests that the team is efficiently allocated to productive tasks, while a low utilization rate signals employee underutilization and the need for proper planning & allocations.
Read More: How to Track Resource Utilization?
Cost Variance
Cost Variance (CV) is calculated to understand the difference between the budgeted cost of work performed, i.e., Earned value, and the actual cost of work performed, i.e., Actual cost. This allows managers to understand the cost efficiency of a project in terms of planning and utilization. The formula to measure this is:
Cost Variance (CV) =
Ideally, the Cost Variance (CV) should be zero, indicating that costs are within the budget. A CV below zero is considered favorable, indicating that the project is under budget, while a CV above zero is unfavorable, signaling a budget overrun.
Schedule Variance
Schedule Variance (SV) measures the difference between the planned schedule and the actual progress of projects over a specified period. This KPI provides insight into whether projects are on schedule, ahead of schedule, or delayed, helping managers identify timeline deviations and take corrective actions, if any. The formula to calculate SV is:
Schedule Variance =
Here, if the Schedule variance (SV) value is zero, the project is on track. An SV value below zero indicates a delay, while an SV above zero signals that the project is progressing ahead of plan.
Employee Turnover Rate
The employee turnover rate is the percentage of the workforce leaving the organization at a particular time – usually annually or quarterly. This also highlights the number of new hires in the firm, allowing managers to make crucial decisions regarding recruitment during capacity planning. The formula to calculate this is:
Employee Turnover Rate =
A higher employee turnover rate signals work dissatisfaction due to reasons like lack of career growth, poor work-life balance, etc. Conversely, a lower employee turnover rate suggests a strong retention strategy driven by growth opportunities, a positive work culture, competitive compensation, etc.
Read More: Employee Retention KPIs: What are They, and Why Tracking Them is Crucial for Firms?
In the following section, we will discuss some key advantages of capacity planning within organizations.
Benefits of Capacity Planning Framework
A robust capacity planning framework contributes to strategic decision-making by offering valuable insights into future capacity requirements, employee availability, and performance trends. This data-driven approach supports long-term planning, ensuring businesses can scale effectively and adapt to market fluctuations.
Additionally, a capacity planning framework also provides firms with a structured approach to managing workforces efficiently, ensuring that the right amount of capacity is available to meet demand without the risk of employee excess/shortage. Further, this framework helps optimize allocation, align workforce and equipment availability with project needs, and ensure timely project initiation within budget.
Finally, implementing a capacity planning framework enhances workforce utilization, ensuring employees are neither overburdened nor underutilized. This reduces the chances of employee burnout and disengagement caused by workload imbalances, conversely increasing workforce productivity rates.
Now, let’s explore the difference between capacity planning and resource planning.
Capacity Planning vs. Resource Planning
While both capacity planning and resource planning help in competent workforce allocation, balancing workloads, maximizing utilization, and meeting goals efficiently, they differ in terms of how it is achieved.
Given below are a few points that help differentiate these two –
| Parameters | Capacity Planning | Resource Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a strategic plan that establishes the total capacity available to meet current & future project demands. | It is a tactical plan that involves scheduling and allocating individuals to specific projects or tasks. |
| Focus | To forecast & ensure people and equipment are available at the right time to prevent resource shortages or excesses. | To ensure the right resources are optimally assigned to projects, enabling timely project execution and delivery. |
| Scope | Broad, focuses on organizational or departmental level planning. | Narrow, focuses on project-level resource allocation. |
| Objective | It helps in bridging demand gaps through hiring, training, etc. | It helps identify the right employees & skills needed for successful project execution |
| Time Horizon | Typically performed for long-term, spanning weeks or months to align with the business plan. | Usually short or medium-term, covering immediate project requirements on a daily or weekly basis. |
| Key Metrics | Standard metrics include forecast accuracy, employee availability, and workforce utilization rates. | A few KPIs are resource allocation efficiency, task completion rate, and time variance. |
Having understood the difference, let’s shift our focus to common challenges of capacity planning.
Read More: 7 Reasons Why You Shouldn’t Use Excel for Resource Planning
Capacity Planning Challenges That Businesses Face
Here are some capacity planning challenges that hinder businesses from meeting demands –
Lack of Real-time Visibility into Capacity and Demand
When managers do not have real-time visibility into upcoming project demands and available workforce capacity, they fail to forward-plan it efficiently. As a result, it may lead to last-minute firefighting, hiring of high-cost employees, loss of billable hours, etc. Thus, a lack of up-to-date data results in inefficient planning, budget overruns, potential project delays, and unmet objectives.
Frequent Hiring/Firing Cycles
When organizations lack a structured capacity planning framework, they often resort to reactive approaches to meet demands, like short-term hiring during peak periods and rapid layoffs during low periods. This increases recruitment and severance costs, disrupts project workflows, and lowers morale, ultimately impacting overall workforce productivity.
Read More: How Resource Management Helps in Reducing the Hiring/Firing Cycle?
Recurring Skill Shortages
As a result of poor capacity planning, managers may not be forewarned about upcoming project demands. Due to this, they will be unable to determine the type of skill sets, competencies, etc., required on time. Thus, they may fail to secure the right people at the right time and are left firefighting for members at critical moments. Ultimately, this leads to lowered productivity, project delays, increased costs, etc.
Increase in Bench Size
When managers perform subpar capacity planning, they may fail to forecast demand or identify employees who will be released from projects in advance. This will result in an increased bench size as employees from multiple projects will be on the bench simultaneously. Over time, this surge in bench size decreases employee engagement, reduces revenue, and increases overhead costs, affecting the company’s bottom line.
Employee Burnout and Unplanned Attrition
When capacity planning is insufficient, managers fail to predict billable and strategic utilization of the workforce ahead of time. Thus, they may end up overburdening a workforce that must consistently operate beyond sustainable levels. This prolonged strain can cause physical and mental fatigue, reducing productivity, morale, and overall job satisfaction. Ultimately, this leads to unplanned attrition, disrupting project continuity and incurring costs.
Read More: How Workforce Planning Prevents Employee Burnout Down the Line?
Next, let’s understand the steps to establish a capacity plan for an organization.
How to Create a Capacity Plan?
A capacity plan helps organizations balance workforce availability with anticipated demand, ensuring optimal utilization.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to developing a capacity plan efficiently –
Assess the Current Capacity
The first step in creating a capacity plan is to thoroughly evaluate your organization’s current capacity to understand the available workforce. Consider factors like employee availability, workloads, and utilization rates to get a clear picture of what the team can realistically handle. By establishing a baseline, firms can ensure that their employees and facilities are optimally allocated to meet ongoing project demands.
Track and Review Employee Skills
This step involves tracking the skills, competencies, qualifications, experience levels, etc., of all employees within the firm. By understanding the current skillset of the workforce, businesses can match the right talent with project needs. Further, conducting skill audits allows firms to identify skill gaps that may require cross-training or upskilling.
Read More: What is Talent Management? A Comprehensive Guide
Determine the Project Requirements
The third step begins with a detailed analysis of project objectives, deliverables, and deadlines. This includes identifying the workforce skillsets, their quantity, and any specialized equipment, technology, or tools that may be essential for the project’s execution. Further, it is also crucial to consider any variability in demand over the course of the project, particularly for long-term or complex initiatives.
Compare Capacity vs. Demand
The fourth step involves performing capacity vs. demand gap analysis and identifying potential gaps. In the case of a workforce deficit, managers can proactively implement training/upskilling programs, employ a backfill/out-rotation strategy, or hire to acquire the necessary skill sets. Conversely, for a workforce surplus, they can adjust project timelines or offer the excess capacity at reduced rates to optimize utilization.

SAVIOM’s powerful Workforce Capacity vs. Demand graph allows managers to quickly assess employee shortage or excess.
Establish and Monitor Capacity Planning KPIs
The next step begins with selecting appropriate capacity planning KPIs such as workforce utilization rates, project completion rates, employee productivity, etc. By defining these relevant KPIs, managers can track performance and identify areas for improvement. Once established, these KPIs should be regularly monitored to assess the effectiveness of the capacity plan.
Read More: 10 Effective Ways to Increase Employee Productivity in the Workplace
Implement the Plan and Monitor it Regularly
This implementation phase ensures the plan is executed with employees assigned to it as per the established priorities and timelines. Regular monitoring involves comparing actual workforce utilization and performance against the forecasted data and KPIs established earlier in the process. This helps identify deviations early and enables timely adjustments for optimal outcomes.
Now that we have learned the steps to create a capacity plan, we shall see some best practices.
Capacity Planning Best Practices
Here are some capacity planning best practices that managers can follow –
Prioritize Projects Based on Criticality
Effective capacity planning requires prioritizing projects based on their strategic importance to the organization. By assessing projects’ criticality, such as alignment with business goals, potential ROI, etc., organizations can allocate the workforce to the most value-driven initiatives first. This way, firms can optimize staff allocations, balance workloads, minimize the risk of delays or missed deadlines, and maintain high-value outcomes.
Refer to Lessons Learned to Improve Forecasting Accuracy
Learning from past projects is crucial for refining capacity planning processes. By systematically reviewing similar past project data, managers can identify recurring challenges, such as workforce bottlenecks or inaccurate time estimates, and use this historical data to enhance forecasting accuracy. This practice allows them to create more realistic project timelines and allocations and mitigate risks early on. Further, combining historical insights improves forecasting accuracy, ultimately enhancing project efficiency.
Leverage a Cross-Functional Team
Cross-functional teams bring together individuals with diverse skills and expertise to work on a project effectively. This collaborative approach offers adaptability, as members can respond to evolving project requirements and fill any skill or knowledge gaps as needed. Consequently, leveraging cross-functional teams enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing project demands, achieve high-quality outcomes, and improve overall project performance.
Read More: 10 Ways to Improve Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Regularly Update the Skill Inventory
Maintaining an up-to-date skill inventory is essential for accurate capacity planning. Organizations should periodically assess and update their employees’ skills, certifications, and experience levels to align with current and future project needs. This practice enables project managers to quickly assess available talent with the right skills. Additionally, an updated skill inventory helps identify skill gaps, allowing for targeted training programs to enhance team capabilities.
Create Contingency Plans for Workforce Risks and Monitor Consistently
Capacity planning should include proactive measures to address workforce risks, such as sudden employee turnover, unplanned absences, or skill shortages. Creating contingency plans, such as cross-training employees or maintaining a pool of temporary staff, can ensure business continuity even when unexpected challenges arise. Further, by regularly monitoring it, firms can detect early warning signs before they escalate, enabling them to maintain stability and operational continuity.
Read More: What is a Contingent Workforce and Why an Organization Needs It?
Use Scenario Planning to Create an Optimal Capacity Plan
Scenario planning is a powerful technique for optimizing capacity plans under varying conditions. By modeling different scenarios, such as a surge in project demand or a sudden employee shortage, changes in workforce availability, etc., managers can anticipate various potential outcomes. This enables them to evaluate potential risks and ensure they are better equipped to handle uncertainties, thereby improving project delivery and workforce efficiency.
Utilize a Robust Capacity Planning Software
A comprehensive capacity planning tool enables firms to forecast employee requirements, bridge demand gaps, optimize workforce allocation, and monitor utilization in real time. Moreover, such software provides advanced analytics and what-if analysis features that allow managers to simulate various scenarios and create efficient capacity plans. Ultimately, this facilitates data-driven decision-making and reduces operational risk in a cost-effective manner.
Next, let’s understand factors that need to be assessed before selecting capacity planning software for an organization.
How to Choose the Right Capacity Planning Software?
It is essential for companies to leverage modern capacity planning software to move beyond limitations.
Given below are some important factors that companies must look into before choosing one –
User Interface & User Experience
When selecting capacity planning software for an organization, the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are critical factors to consider. A well-designed UI ensures that the software is intuitive, easy to navigate, and accessible to all users. Similarly, a strong UX ensures that it aligns with the user’s workflow, reducing the learning curve and enhancing satisfaction.
Configurability & Scalability
Businesses must select scalable and configurable capacity planning software to meet current needs and expandable to meet future business requirements. Furthermore, the system should be able to support and accommodate a growing user base without compromising response time and performance. This, in turn, provides long-term value and support to accomplish strategic objectives.
Critical Business Functionalities
A good capacity planning tool must support comprehensive resource management processes, including forecasting, scheduling, utilization, and optimization. Further, it should also offer additional features that support these processes, like 360-degree visibility, multidimensional schedulers, Gantt-chart view, advanced filters, an automated resource requisition workflow, etc. Together, these features allow companies to manage the workforce, anticipate challenges, and make informed decisions.
Support for Matrix Organizational Structure
Companies should have capacity planning software that seamlessly aligns with the complexities of a matrix organization. The software must offer visibility into workforce allocation across multiple projects and departments. This feature ensures effective management of a shared workforce, reducing conflicts and improving collaboration between different teams. It enhances visibility into employee assignments, making it easier to balance priorities.
Real-time Dashboard, Reports & Analytics
In a dynamic business environment, project demand changes constantly. Hence, it is crucial to get real-time business intelligence through reports, analytics, and dashboards. The software must offer insights into capacity and demand that help with capacity planning and prevent under/over-staffing. Further, analytics and dashboards can also highlight potential risks and mitigate them effectively.

SAVIOM’s advanced Workforce Capacity vs. Demand BI dashboard allows managers to forecast demand gaps by Team, Resource, and Primary Role.
Modeling and Simulation Features
The tool must include modeling and simulation modules, also known as what-if analysis functionality, to explore diverse scenarios within existing constraints. This feature enables managers to analyze the impact of various scenarios on factors like availability, capacity, cost, etc. Thus, businesses can prioritize the most profitable capacity plans to meet organizational goals.
Read More: 5 Benefits of Using Business Intelligence in Resource Management
Integration with Existing Applications
Effective integration ensures that the new software can work harmoniously with the organization’s current applications like ERP, CRM, project management tools, or HR systems. This capability provides a unified view of your workforce and project data, enables data synchronization across platforms, reduces manual entry, and minimizes errors.
Total Cost of Ownership
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) encompasses not only the initial purchase cost but also all associated costs like licensing fees, maintenance & support fees, customization costs, etc., over the software’s lifecycle. By considering TCO, firms can assess the full financial impact of adopting the capacity planning software and ensure that the investment is sustainable in the long term and delivers true value.
Read More: How Scott Automation Redefined Resource Forecasting with SAVIOM?
Final Thoughts
Effective capacity planning is crucial for maximizing employee utilization, reducing costs, and ensuring business continuity. By forecasting and aligning the workforce with demand, organizations can boost operational efficiency, improve decision-making, and foster sustainable growth.
Further, by adopting best practices and leveraging the right tools, businesses can navigate complexities, manage risks, and achieve their strategic objectives with greater agility and precision.
Book a 60-day customized trial with SAVIOM today!
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management










